Windows 11 BitLocker encrypted files accessed? Yeah, we get it – data security is serious business. But navigating the ins and outs of BitLocker encryption doesn’t have to be a headache. This guide breaks down everything you need to know about accessing your encrypted files, from understanding the different encryption methods to troubleshooting common issues. We’ll even cover those sneaky security vulnerabilities and how to avoid becoming the next victim of a digital heist. Buckle up, it’s going to be a ride.
Whether you’re a tech whiz or just trying to keep your personal files safe, understanding BitLocker is crucial in today’s digital world. This comprehensive guide dives deep into the process of accessing your encrypted files, providing clear, step-by-step instructions and helpful tips. We’ll cover various unlocking methods, recovery key management, and even address potential security vulnerabilities. By the end, you’ll be a BitLocker boss.
BitLocker Drive Encryption Overview
BitLocker Drive Encryption, a built-in feature in Windows 11, provides robust data protection by encrypting your entire hard drive or removable storage device. This ensures that only authorized users with the correct decryption key can access the data, safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access, even if the device is lost or stolen. It’s a crucial tool for anyone concerned about data security, particularly those handling sensitive personal or business information.
BitLocker employs various encryption algorithms to scramble your data, making it unreadable without the appropriate decryption key. This key is typically stored on a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) chip, a hardware component designed to securely store cryptographic keys. The level of security offered by BitLocker depends on the chosen encryption mode and the configuration of your system.
BitLocker Encryption Modes
BitLocker offers several encryption modes, each providing a different level of security and requiring varying levels of system configuration. The choice of mode depends on the security needs and the hardware capabilities of the computer. Understanding the differences is crucial for implementing the appropriate level of protection.
Enabling BitLocker Encryption
Enabling BitLocker is a straightforward process, though it requires careful consideration of the chosen encryption mode and backup strategy. Losing your recovery key renders your data inaccessible.
1. Open BitLocker Drive Encryption: Navigate to the Control Panel, then to System and Security, and finally click on BitLocker Drive Encryption.
2. Select the Drive: Choose the drive you wish to encrypt (usually the system drive (C:)).
3. Choose an Encryption Method: Select the desired encryption method (AES-128 or AES-256). AES-256 is generally recommended for stronger security.
4. Choose a Password or Smart Card: You’ll need to create a password or use a smart card to unlock the drive. This password is crucial; lose it, and you lose access to your data.
5. Save the Recovery Key: BitLocker will provide a recovery key. This is absolutely essential. Save it securely in multiple locations, such as a printed copy, a USB drive, or a cloud storage service. This key is your lifeline if you lose access to your encrypted drive.
6. Start Encryption: Initiate the encryption process. The time required depends on the size of the drive and system performance. During this time, the system will remain usable, although performance might be slightly impacted.
Comparison of BitLocker Encryption Methods
The strength of BitLocker encryption primarily depends on the chosen encryption algorithm and the use of additional security features. AES-256 offers significantly stronger protection than AES-128.
| Encryption Method | Key Size (bits) | Security Strength | TPM Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| AES-128 | 128 | Moderate | Recommended |
| AES-256 | 256 | High | Recommended |
Accessing Encrypted Files
So, your files are safely tucked away behind BitLocker’s encryption. That’s great for security, but how do you actually get to them when you need them? Let’s break down the process of accessing your precious data on your Windows 11 machine. It’s easier than you might think, but understanding the different methods and their security implications is key.
Accessing your BitLocker-encrypted files involves unlocking the drive containing those files. This requires providing the correct authentication credentials, which depends on the unlock method you’ve chosen during the encryption process. Incorrect credentials will prevent access, maintaining the security of your data. Let’s delve into the specifics.
BitLocker Unlock Methods and Their Security Implications
The security of your data directly correlates with the chosen unlock method. Stronger methods offer better protection against unauthorized access, while weaker methods offer convenience at the cost of reduced security. Choosing the right method depends on your risk tolerance and the sensitivity of your data.
- Password: This is the most common method. A strong, unique password provides a good level of security, but it’s only as strong as the password itself. Guessable passwords significantly weaken the protection. Consider using a password manager to generate and securely store complex passwords.
- PIN: Similar to a password, but uses a numerical code. While convenient, shorter PINs are more susceptible to brute-force attacks. A longer PIN offers better security.
- Smart Card: This method uses a physical smart card to authenticate. It’s generally considered more secure than passwords or PINs, as the card itself needs to be physically present.
- USB Drive: A USB drive containing a BitLocker startup key provides another layer of security. The key needs to be physically inserted to unlock the drive. Losing this drive renders your data inaccessible, highlighting the importance of secure storage.
- Trusted Platform Module (TPM): The TPM is a hardware security chip built into many modern computers. It can be used in conjunction with other methods (like a password) to add an extra layer of protection. This method offers robust security but relies on the integrity of the TPM itself.
Accessing Encrypted Files with a Password: A Step-by-Step Flowchart
Imagine this flowchart as a visual guide to unlocking your BitLocker-encrypted drive using a password.
[Description of Flowchart: The flowchart would start with a box labeled “Attempt to Access Encrypted Drive.” An arrow would lead to a decision box: “Correct Password Entered?”. If yes, an arrow leads to “Drive Unlocked; Access Granted.” If no, an arrow leads to “Incorrect Password. Try Again.” After several incorrect attempts, an arrow would lead to “Drive Locked; Contact Administrator”.]
Recovery Key Management
Your BitLocker recovery key is the ultimate insurance policy for your encrypted data. Losing it means losing access to everything on your drive – a scenario you definitely want to avoid. Proper management of this key is crucial for both data security and peace of mind. Think of it as the combination to your digital vault; keep it safe, and your valuables are secure.
The importance of secure recovery key storage cannot be overstated. This key is your only way back into your encrypted drive if you forget your password, your system malfunctions, or the drive is replaced. A compromised key grants unauthorized access to all your sensitive data, potentially leading to significant financial and reputational damage. Think of the consequences – lost business data, compromised personal information, or even identity theft. The stakes are high.
Secure and Insecure Recovery Key Storage Methods
Storing your BitLocker recovery key securely requires careful consideration. A simple approach, but one that’s surprisingly risky, is saving it to a local file. This makes it vulnerable to malware or unauthorized access if your computer is compromised. Similarly, emailing the key to yourself is highly discouraged, as emails can be intercepted. These methods offer minimal security.
Better options include using a dedicated password manager that employs strong encryption, storing it on a secure, offline physical device (like a printed copy kept in a safe), or using a cloud-based service specifically designed for secure key storage. Consider the potential vulnerabilities of each method before choosing. A printed copy, for instance, can be lost or stolen, while cloud services need to be carefully vetted for their security protocols.
Implications of Losing the BitLocker Recovery Key
Losing your BitLocker recovery key is essentially losing access to your encrypted drive. There’s no backdoor, no alternative method to bypass the encryption. Data recovery is impossible without the key. This means irretrievable loss of all files and applications stored on the drive. For businesses, this translates to lost productivity, potential financial penalties for missed deadlines, and damage to reputation. For individuals, it could mean the loss of irreplaceable photos, documents, and other important personal information. The impact is severe and potentially devastating.
Best Practices for Recovery Key Management
The best approach to recovery key management involves a multi-layered strategy. First, choose a strong, unique password for your BitLocker encryption. Second, select a secure storage method, ideally using a combination of techniques. For example, store a copy in a secure password manager, print a copy and keep it in a fireproof safe at a separate location, and consider storing another copy in a trusted cloud storage service with strong multi-factor authentication. Regularly back up your recovery key and ensure its security. Lastly, understand the implications of losing the key and plan accordingly – consider the potential impact on your personal and professional life, and ensure you have robust disaster recovery plans in place.
Potential Security Vulnerabilities
BitLocker, while a robust encryption solution, isn’t impenetrable. Like any security measure, it has vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit, potentially compromising your data. Understanding these weaknesses is crucial for implementing effective mitigation strategies and maintaining the integrity of your encrypted files. This section will explore potential attack vectors and methods to minimize their impact.
While BitLocker significantly enhances data security at rest, several scenarios can potentially lead to data breaches. These vulnerabilities range from physical attacks to sophisticated software exploits, each demanding a layered security approach to effectively counter. Understanding these vulnerabilities is the first step toward robust data protection.
Physical Attacks
Physical access to a BitLocker-encrypted device presents a significant risk. An attacker with physical access can potentially bypass BitLocker through various methods. For example, they could attempt to cold boot the system to access the encryption key in RAM before it’s overwritten. Another method involves using specialized hardware to extract the encryption key directly from the device’s storage. Furthermore, a determined attacker might attempt to steal the recovery key, either physically or through social engineering. Mitigating this risk requires strong physical security measures, such as secure storage, and robust password management practices. The use of TPM (Trusted Platform Module) adds a layer of protection against such attacks, making it harder to access the encryption key even with physical access.
Software Vulnerabilities
Software vulnerabilities in the operating system or BitLocker itself can be exploited by attackers to gain access to encrypted data. These vulnerabilities might allow an attacker to execute malicious code with elevated privileges, potentially allowing them to bypass the encryption process or steal the encryption key. Regular updates to the operating system and BitLocker are crucial to patching known vulnerabilities. Employing a robust security posture, including firewalls and intrusion detection systems, can further mitigate the risk of software-based attacks. Regular security audits and penetration testing can also identify potential vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
Social Engineering
Social engineering attacks can be used to trick users into revealing their BitLocker recovery key or other sensitive information. Phishing emails, pretexting, and other social engineering techniques can be effective in gaining access to the recovery key, thus bypassing the encryption. User education is paramount in mitigating this risk. Regular training on recognizing and avoiding social engineering tactics is crucial for preventing these attacks. Implementing strong password policies and multi-factor authentication (MFA) can add further layers of protection against unauthorized access.
Bootloader Attacks
Malicious actors could attempt to modify the system’s bootloader to gain access before BitLocker is activated. This could involve replacing the legitimate bootloader with a malicious one, allowing the attacker to bypass the encryption process entirely. Secure boot features, coupled with regular updates to the system firmware, are essential to prevent this type of attack. Maintaining up-to-date antivirus software and regularly scanning for malware are also important preventative measures. Employing a secure boot process, which verifies the integrity of the boot process before loading the operating system, significantly reduces the risk of bootloader attacks.
Mitigation Strategies
Implementing a comprehensive security strategy is essential to minimize the risk of BitLocker vulnerabilities. This includes regular software updates, strong password policies, multi-factor authentication, robust physical security measures, and employee training on security awareness. Furthermore, regular backups of encrypted data can provide a recovery mechanism in case of a successful attack. By employing a layered security approach, organizations can significantly enhance the protection of their BitLocker-encrypted data.
BitLocker and System Performance
Enabling BitLocker encryption adds a layer of security, but it inevitably impacts your system’s performance. The extent of this impact depends on several factors, including the type of drive, the amount of data being encrypted, and the system’s hardware capabilities. While the performance hit might be negligible on powerful machines with fast SSDs, older systems or those with slower hard drives can experience noticeable slowdowns. Understanding this trade-off is crucial for making informed decisions.
BitLocker’s performance overhead stems from the cryptographic operations involved in encrypting and decrypting data. Every read and write operation requires additional processing power to handle the encryption and decryption processes. This adds latency to file access, resulting in slower boot times, application loading, and overall system responsiveness. The impact is most noticeable during disk-intensive tasks like large file transfers or database operations.
Performance Overhead in Different Scenarios
The performance impact of BitLocker varies considerably depending on several factors. Here’s a table illustrating potential overhead in different scenarios. Note that these figures are estimations and actual performance will vary based on specific hardware and software configurations.
| Scenario | Boot Time Increase | File Access Latency | Overall System Responsiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-end SSD, Modern CPU | Minimal (seconds) | Slightly noticeable | Generally unaffected |
| Mid-range HDD, Older CPU | Noticeable (minutes) | Significant | Appreciably slower |
| Low-end HDD, Older CPU | Significant (minutes) | Very significant | Severely impacted |
| High-end NVMe SSD, Modern CPU | Negligible | Minimal | Barely noticeable |
Strategies for Optimizing System Performance with BitLocker
Several strategies can mitigate the performance impact of BitLocker. Choosing a fast storage device like an NVMe SSD significantly reduces the overhead compared to using a traditional HDD. Keeping your system’s hardware up-to-date with sufficient RAM and a powerful processor also helps. Additionally, regularly defragmenting your hard drive (if using an HDD) can improve performance, although this is less critical with SSDs. Finally, consider using BitLocker’s “Used Space Only” encryption option, which encrypts only the used space on the drive, reducing the overall encryption overhead. However, keep in mind that this option leaves unallocated space unencrypted, which presents a potential security risk.
The Security-Performance Trade-off, Windows 11 bitlocker encrypted files accessed
Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to use BitLocker involves a trade-off between security and performance. The added security of BitLocker’s encryption comes at the cost of some performance reduction. The degree of this trade-off is heavily dependent on the hardware and software used. For systems where data security is paramount, even a significant performance decrease might be acceptable. However, in situations where performance is critical, alternative security measures or a less stringent encryption method might be considered. The balance between security and performance needs to be carefully evaluated based on the specific needs and constraints of each situation.
BitLocker Integration with Other Security Features: Windows 11 Bitlocker Encrypted Files Accessed
Source: groovypost.com
BitLocker doesn’t operate in a vacuum; its effectiveness is significantly boosted when combined with other robust security measures built into Windows 11. Think of it as a powerful engine needing a well-tuned chassis for optimal performance. This integration creates a layered security approach, offering comprehensive protection against data breaches.
BitLocker’s strength lies in its ability to seamlessly integrate with various Windows 11 security features, creating a more resilient and secure environment. This synergy enhances data protection beyond what any single feature could achieve alone, offering a robust defense against unauthorized access. This integration is not just additive; it’s synergistic, creating a whole greater than the sum of its parts.
BitLocker and Windows Hello for Business
Windows Hello for Business provides multi-factor authentication, using biometric data like fingerprints or facial recognition, or a PIN, for user authentication. When combined with BitLocker, this creates a strong two-layered security system. The user must first authenticate themselves via Windows Hello for Business before accessing the BitLocker-encrypted drive. This prevents unauthorized access even if someone physically obtains the device. For example, even if a thief steals a laptop, they cannot access the encrypted data without the correct biometric or PIN authentication, making data theft significantly more difficult. This layered approach dramatically reduces the risk of data breaches compared to relying on just BitLocker or just Windows Hello for Business.
BitLocker and Device Guard
Device Guard is a Windows 11 security feature that enhances system security by limiting what software can run on a device. It works by creating a controlled environment where only trusted applications and processes can execute. Integrating BitLocker with Device Guard provides a comprehensive security posture. While BitLocker protects data at rest, Device Guard protects the system itself from malicious software that could potentially compromise the encryption key or exploit vulnerabilities to access encrypted data. Imagine a scenario where malware tries to infect the system: Device Guard prevents its execution, while BitLocker protects the data even if a breach occurs. The combined effect significantly reduces the risk of both data theft and system compromise.
BitLocker and Credential Guard
Credential Guard protects user credentials, such as passwords and domain credentials, by isolating them in a secure virtualized environment protected by virtualization-based security (VBS). This prevents attackers from accessing these credentials even if they compromise the operating system. When used with BitLocker, this creates a multi-layered security approach. BitLocker protects data at rest, while Credential Guard protects user credentials from being stolen or used to access the encrypted data. This means even if an attacker gains access to the system, they cannot easily access the encrypted data because they lack the necessary credentials, further enhancing data security. The combined use of both technologies significantly enhances security compared to using either one individually.
Benefits of Combined Security Measures
The benefits of using BitLocker in conjunction with other security tools are numerous. This layered approach significantly improves data protection by providing multiple layers of defense against unauthorized access and data breaches. It strengthens the overall security posture of the system, making it far more resilient against sophisticated attacks. The combined use of BitLocker and other security features provides a significantly higher level of protection than relying on a single security measure. This layered approach minimizes vulnerabilities and increases the overall security of sensitive data.
Troubleshooting BitLocker Issues
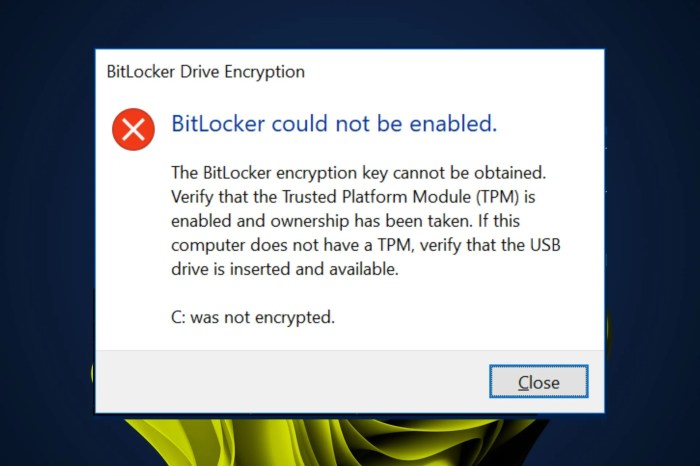
Source: windowsreport.com
BitLocker, while a robust security feature, isn’t immune to hiccups. From simple user errors to more complex system malfunctions, encountering problems is a possibility. Understanding common issues and their solutions can save you significant time and frustration. This section Artikels common BitLocker problems, their causes, and effective troubleshooting steps.
Common BitLocker Issues and Their Causes
BitLocker problems often stem from incorrect user actions, hardware failures, or software conflicts. For example, a forgotten recovery key is a frequent culprit, leaving you locked out of your encrypted drive. Hardware issues, such as a failing hard drive, can also trigger BitLocker errors, preventing access to your data. Software conflicts, particularly with third-party security software, can sometimes interfere with BitLocker’s operation, leading to unexpected behavior. Incorrect system configurations during BitLocker setup can also lead to difficulties accessing encrypted data.
Troubleshooting Steps for Resolving Common BitLocker Problems
The first step in troubleshooting is identifying the specific error message. This provides crucial clues about the problem’s nature. If you’ve forgotten your recovery key, Microsoft provides tools and methods to regain access, usually involving proving ownership of the computer. If a hardware problem is suspected, running a diagnostic check on your hard drive is crucial. For software conflicts, temporarily disabling other security software can help determine if it’s the root cause. If the issue persists after these steps, checking the BitLocker settings within Windows to ensure the correct configuration can be the next step. A system restore to a point before the problem began might also resolve the issue.
BitLocker Error Messages and Their Explanations
BitLocker generates specific error codes to help pinpoint the problem. For example, an error indicating “The BitLocker drive is unavailable” often points to a hardware failure or a problem with the drive’s partition. An error stating “The recovery key is required” clearly indicates that the recovery key is needed to access the drive. Understanding these messages is key to effective troubleshooting. Microsoft’s support documentation provides detailed explanations for various BitLocker error codes, making accurate diagnosis easier.
Resources for Further Troubleshooting Assistance
Numerous resources are available to help resolve BitLocker issues. Microsoft’s official support website offers comprehensive troubleshooting guides, FAQs, and detailed explanations of error codes. Online forums dedicated to Windows and security issues often contain discussions and solutions contributed by other users. Consider searching for specific error messages on these platforms to find potential solutions. Additionally, contacting Microsoft support directly provides access to expert assistance for more complex problems.
BitLocker in Enterprise Environments
BitLocker, Microsoft’s full disk encryption tool, isn’t just for home users; it’s a crucial component of a robust security strategy for large organizations. Its ability to protect sensitive data at rest, even against physical theft or unauthorized access, makes it a vital asset in safeguarding company information and maintaining compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. Implementing BitLocker effectively across an enterprise, however, requires careful planning and execution.
Deploying and managing BitLocker across a large organization demands a systematic approach. This goes beyond simply enabling it on individual machines; it necessitates centralized control, automated deployment, and efficient key management. Failure to properly manage BitLocker can lead to significant security risks and operational headaches. The right strategy minimizes downtime and ensures consistent security across the entire enterprise.
BitLocker Deployment Strategies
Several strategies exist for deploying BitLocker in enterprise environments. These range from manual configuration on individual machines to fully automated deployments leveraging tools like Microsoft Endpoint Manager (Intune) and System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM). Automated deployments significantly reduce the administrative burden associated with managing encryption across hundreds or thousands of devices. Consider factors such as the size of the organization, existing infrastructure, and technical expertise when choosing a deployment method. A phased rollout, starting with a pilot program in a smaller department, can help identify and resolve potential issues before a full-scale deployment.
Managing BitLocker with Group Policy
Group Policy provides centralized control over BitLocker settings within an Active Directory environment. Administrators can use Group Policy Objects (GPOs) to configure encryption requirements, specify allowed recovery methods, and enforce security policies consistently across all managed devices. This allows for granular control, enabling organizations to tailor BitLocker settings to different user groups or departments based on their specific security needs. For instance, a highly sensitive department might require stronger encryption methods or more stringent recovery key management than a less sensitive one. Properly configured GPOs ensure compliance and minimize the risk of inconsistent security practices.
Considerations for Enterprise BitLocker Deployment
Before implementing BitLocker enterprise-wide, several factors must be considered. These include:
- Hardware Compatibility: Ensure all devices meet the minimum hardware requirements for BitLocker. Older hardware might not support the necessary features, requiring upgrades or exemptions.
- Operating System Compatibility: Verify that all operating systems in use are compatible with the desired BitLocker features and settings. Older OS versions might have limited support.
- Recovery Key Management: Establish a robust recovery key management system to prevent data loss in case of forgotten passwords or hardware failures. This might involve using a centralized key management system or employing multiple recovery methods.
- User Training: Provide comprehensive training to users on BitLocker’s functionality, including how to manage their recovery keys and troubleshoot potential issues. This minimizes support requests and ensures user adoption.
- Performance Impact: Evaluate the potential performance impact of BitLocker on different devices and workloads. While generally minimal, encryption can affect boot times and disk I/O performance, especially on older or less powerful hardware.
- Integration with other security tools: Ensure BitLocker integrates seamlessly with other security tools and technologies in use, such as antivirus software and intrusion detection systems. This creates a more comprehensive security posture.
- Compliance Requirements: Understand and comply with relevant industry regulations and legal requirements related to data encryption and security. BitLocker’s configuration should align with these standards.
End of Discussion
Source: ubackup.com
So, there you have it – your ultimate guide to conquering Windows 11 BitLocker encrypted files. From initial setup and unlocking methods to advanced security considerations and troubleshooting tips, we’ve covered the essentials. Remember, keeping your data secure is paramount, so understanding and effectively managing your BitLocker encryption is key. Now go forth and conquer those encrypted files! And don’t forget to back up your recovery key!