Microsoft multi factor authentication issue – Microsoft Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) issues? Yeah, we’ve all been there. That frustrating moment when you’re locked out of your Microsoft account, your productivity grinds to a halt, and you’re left staring blankly at an error message. This guide dives deep into the most common problems, from user errors to admin headaches, offering practical solutions and preventative measures to keep you smoothly sailing through your workday. We’ll cover everything from troubleshooting specific Microsoft products like Microsoft 365 and Azure, to understanding the security implications of MFA failures and securing your mobile devices. Get ready to conquer those MFA hurdles!
This comprehensive guide tackles the complexities of Microsoft MFA problems, providing clear explanations, step-by-step instructions, and preventative strategies. Whether you’re a user struggling with authentication app issues or an administrator dealing with widespread MFA failures, you’ll find the answers you need here. We’ll explore the unique challenges posed by different Microsoft platforms, address user-side errors, and delve into the crucial role of administrators in maintaining a secure MFA system. By the end, you’ll be equipped to handle any MFA issue that comes your way.
Common Microsoft Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Problems
Microsoft Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) significantly boosts security, but it’s not without its hiccups. Navigating MFA issues can be frustrating, especially when you’re trying to access crucial work resources or personal accounts. This section dives into five common problems and offers practical troubleshooting steps to get you back online swiftly.
Five Prevalent MFA Issues and Their Solutions
MFA problems often stem from simple user errors, outdated software, or network connectivity glitches. Understanding these common issues and their solutions can save you considerable time and stress. The table below Artikels five prevalent problems, their causes, solutions, and preventative measures.
| Problem |
Cause |
Solution |
Prevention |
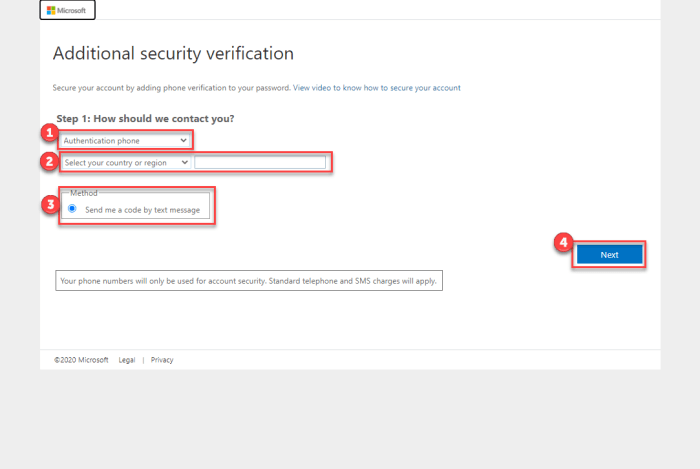
| Incorrect Authentication Method Selection |
Choosing the wrong authentication method (e.g., selecting email when you usually use an authenticator app). |
Carefully review the available authentication options and select the correct method. If you’ve forgotten your chosen method, you might need to use a recovery method (like a security question or alternate email). Contact your IT administrator if you are locked out and cannot recover access. |
Always double-check the selected authentication method before proceeding. Consider using only one or two consistent methods to reduce confusion. |
| Authenticator App Issues |
Problems with the authenticator app itself, such as a faulty installation, outdated version, or synchronization problems. This might result in the app not generating codes correctly or failing to connect to Microsoft services. Error messages might include “Verification code incorrect” or “App not responding”. |
Reinstall the authenticator app, ensure it’s updated to the latest version, and check your device’s time and date settings. If the problem persists, try a different device or a different authenticator app (like Google Authenticator or Authy). |
Regularly update your authenticator app. Ensure your device’s time and date are accurately synchronized. Consider using multiple authenticator apps for redundancy. |
| Network Connectivity Problems |
Inability to connect to the internet or Microsoft servers. This often results in timeouts or failure to receive authentication codes. Error messages might include “Connection timed out” or “Cannot connect to server”. |
Check your internet connection. Restart your device and router. If using a VPN, temporarily disable it to see if it resolves the issue. Contact your network administrator if the problem persists. |
Ensure a stable and reliable internet connection is always available. |
| Forgotten Recovery Methods |
Losing access to recovery methods like registered email addresses or phone numbers. This can leave you locked out of your account if MFA is required. |
Before you get locked out, update your recovery information regularly. If already locked out, contact Microsoft support or your IT administrator to initiate account recovery. This process usually involves verifying your identity through various security checks. |
Regularly review and update your recovery information. Store this information securely in a password manager but not as the password itself. |
| Incorrect Password Entry |
Simply entering the wrong password. This is a common issue that prevents the MFA process from even starting. Error messages will typically indicate an incorrect password. |
Carefully re-enter your password, ensuring correct capitalization and characters. If you’ve forgotten your password, use the password reset feature provided by Microsoft. |
Use a strong and unique password, and consider using a password manager to securely store and manage your credentials. |
MFA Issues Related to Specific Microsoft Products

Source: b-cdn.net
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a crucial security measure, but its implementation and troubleshooting can vary significantly depending on the specific Microsoft product you’re using. Understanding these nuances is key to a smooth and secure experience. This section dives into the common MFA problems encountered in Microsoft 365, Azure, and Intune, providing tailored troubleshooting strategies for each.
Microsoft 365, Azure, and Intune, while interconnected, have unique approaches to MFA. Their differences stem from their distinct functionalities and target audiences. Microsoft 365 focuses on productivity apps, Azure on cloud infrastructure, and Intune on mobile device management. These differences lead to varied MFA implementation methods and troubleshooting needs.
MFA Implementation and Common Issues Across Microsoft 365, Azure, and Intune
The core functionality of MFA remains consistent across these platforms—verifying user identity through multiple factors—but the methods and potential issues differ. Microsoft 365 typically uses methods like authenticator apps, SMS codes, or security keys integrated directly into the user experience. Azure, on the other hand, offers more granular control and integration with various authentication providers, potentially leading to more complex configurations and troubleshooting scenarios. Intune leverages MFA to secure access to company resources on mobile devices, introducing unique challenges related to device enrollment and compliance policies. Common issues include incorrect password entries, network connectivity problems impacting authentication requests, and issues with the MFA method itself (e.g., authenticator app malfunctions).
Troubleshooting Approaches for Microsoft 365
Troubleshooting MFA issues in Microsoft 365 often involves verifying the user’s account status, checking for password resets or account lockouts, and ensuring that the MFA methods are correctly configured.
- Verify user account status: Check if the account is enabled, unlocked, and assigned the correct license.
- Check password resets and account lockouts: Frequent incorrect password entries can trigger account lockouts, preventing MFA from working. Resetting the password might resolve the issue.
- Confirm MFA method configuration: Ensure the user has enrolled in a suitable MFA method and that the method is functioning correctly. This might involve checking the authenticator app, verifying phone number accuracy, or testing a security key.
- Examine Microsoft 365 admin center logs: The admin center provides detailed logs that can pinpoint the specific point of failure during the authentication process.
Troubleshooting Approaches for Azure
Azure’s more intricate MFA configuration necessitates a deeper dive into its settings and integration with other services.
- Review Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) settings: Verify that MFA is correctly enabled for the specific users, groups, or applications.
- Check Azure AD Connect health: If using on-premises Active Directory, ensure Azure AD Connect is functioning correctly and synchronizing user information properly.
- Inspect Azure AD conditional access policies: These policies define the conditions under which MFA is required. A misconfigured policy can prevent access even with correct credentials.
- Examine Azure Monitor logs: Similar to Microsoft 365, Azure Monitor offers detailed logs to identify MFA-related issues.
Troubleshooting Approaches for Intune
Intune’s MFA troubleshooting often involves verifying device compliance and the user’s enrollment status.
- Confirm device compliance: Intune might block access if the device doesn’t meet specified compliance policies (e.g., requiring a passcode or device encryption).
- Check user enrollment status: Ensure the user is correctly enrolled in Intune and that their device is properly registered.
- Review Intune policies: Intune policies can dictate MFA requirements for specific apps or resources. Verify that these policies are appropriately configured and applied.
- Examine Intune logs: Intune provides detailed logs to assist in identifying problems related to MFA and device management.
Troubleshooting MFA Problems in Microsoft Teams
A flowchart can simplify troubleshooting MFA issues within Microsoft Teams.

Source: wilkinsit.ca
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) relies heavily on mobile devices for its second factor, often using authentication apps or SMS codes. This convenience, however, introduces a unique set of challenges, primarily revolving around the inherent vulnerabilities of mobile devices themselves. Losing your phone, experiencing app malfunctions, or facing a compromised device can all disrupt your access to crucial accounts and systems. Understanding these risks and having a recovery plan in place is vital for maintaining secure access.
Mobile devices, while convenient for MFA, present several potential vulnerabilities. Lost or stolen phones immediately compromise your MFA access, as the authentication app or the ability to receive SMS codes is gone. Similarly, app malfunctions, software glitches, or even a simple phone reboot can temporarily or permanently disable your ability to authenticate. These situations necessitate robust recovery mechanisms and proactive security measures.
Recovering Access After Mobile Device Loss or Compromise
Recovering access after losing or compromising your mobile device requires immediate action. First, report the loss or theft to your mobile carrier to prevent unauthorized access and potential fraud. Then, contact your organization’s IT help desk or the support team for the affected services. They will likely guide you through a recovery process, which might involve verifying your identity through alternative methods, such as security questions or a secondary contact. In some cases, they may require you to reset your password and re-enroll your new device for MFA. Acting quickly minimizes the window of vulnerability.
Enrolling and Unenrolling a Mobile Device from MFA
Properly enrolling and unenrolling your mobile device is crucial for maintaining secure MFA. These steps ensure that only authorized devices can access your accounts. Incorrect procedures can leave you vulnerable.
- Enrollment: Typically, you’ll begin by logging into your account’s security settings. Then, select the option to add a new MFA method. Choose your preferred method (authentication app, SMS, etc.). Follow the on-screen instructions, which usually involve downloading an authentication app (like Microsoft Authenticator or Google Authenticator), scanning a QR code, or entering a verification code sent to your phone. Once the process is complete, test your new MFA setup by attempting to log in.
- Unenrollment: If you lose or replace your device, or simply want to remove it from your MFA setup, you’ll again need to access your account’s security settings. Locate the section managing your MFA methods. Select the mobile device you wish to remove. The process will likely involve confirmation steps to ensure it’s you performing the action. After successful unenrollment, your selected device will no longer be used for MFA authentication. Immediately add a new, trusted device to avoid service interruptions.
Integrating MFA with Third-Party Applications
Source: amazonaws.com
Extending the security of Microsoft’s robust multi-factor authentication (MFA) to third-party applications is crucial for a truly secure digital environment. This process, however, isn’t always a smooth ride, and understanding the nuances is key to avoiding headaches down the line. Let’s dive into the hows and whys.
Integrating Microsoft MFA with third-party applications typically involves leveraging protocols like SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) or OpenID Connect (OIDC). These protocols act as bridges, allowing your third-party apps to communicate securely with Microsoft’s authentication system. The specific implementation details vary depending on the application, but generally involve configuring settings within both the Microsoft Azure portal and the third-party application itself. This often includes registering the application with Azure Active Directory, defining user roles and permissions, and configuring the appropriate authentication flows. Think of it like setting up a secure handshake between two different systems.
Compatibility Issues During MFA Integration, Microsoft multi factor authentication issue
Different third-party applications have varying levels of support for Microsoft MFA integration. Some applications might seamlessly integrate using standard protocols like SAML or OIDC, while others may require custom integrations or workarounds. Older or less-maintained applications might lack the necessary support altogether, presenting a significant challenge. The complexity of the application’s architecture and its reliance on legacy systems can also contribute to integration difficulties. For example, an application built on an outdated framework might not be able to handle the security protocols required for seamless MFA integration. This often necessitates a deeper investigation into the application’s capabilities and potentially a conversation with the application’s vendor or support team.
Comparison of Integration Processes for Different Third-Party Applications
The process of integrating Microsoft MFA varies significantly depending on the third-party application. Here’s a comparison of three popular application types:
| Application Type |
Integration Method |
Typical Challenges |
| Cloud-based SaaS Application (e.g., Salesforce) |
Usually supports SAML or OIDC, often with pre-built connectors in Azure AD. Configuration primarily involves setting up trust relationships and defining user mappings. |
Mismatched attribute mappings between Azure AD and the SaaS application can lead to authentication failures. Ensuring proper user provisioning and de-provisioning is also crucial. |
| On-premises Application (e.g., legacy line-of-business application) |
Often requires custom development or the use of a third-party identity provider that acts as an intermediary. This typically involves more complex configuration and potentially higher costs. |
Requires expertise in both Microsoft technologies and the specific on-premises application. Maintaining compatibility with future updates to both systems can be a challenge. |
| Mobile Application (e.g., a custom-built iOS or Android app) |
Might use Microsoft Authentication Libraries (MSAL) to integrate directly with Azure AD. This requires developers to integrate the libraries into the app’s codebase. |
Requires skilled developers familiar with MSAL and the specific mobile platform. Managing different authentication flows for various mobile platforms can be complex. |
Best Practices for MFA Implementation and Maintenance: Microsoft Multi Factor Authentication Issue
Implementing and maintaining a robust multi-factor authentication (MFA) system is crucial for securing your Microsoft environment. A well-structured approach minimizes vulnerabilities and ensures a smooth user experience. Neglecting this aspect can leave your organization exposed to significant security risks. This section Artikels best practices to fortify your MFA strategy.
MFA Policy Review and Updates: Frequency and Scope
Regular reviews of your MFA policies are essential to adapt to evolving threats and technological advancements. A minimum of twice-yearly reviews is recommended, with more frequent checks (quarterly or even monthly) for organizations handling highly sensitive data or experiencing frequent security incidents. These reviews should assess the effectiveness of current MFA methods, examine user adoption rates, and identify potential weaknesses. Updates should include adjusting authentication methods based on risk profiles, incorporating new authentication technologies, and refining access control based on user roles and responsibilities. For example, a company experiencing a phishing attack might strengthen its MFA policy by mandating stronger password complexity requirements and adding a time-based one-time password (TOTP) method.
Checklist for MFA Policy Review and Updates
Prior to initiating any MFA policy review or update, a structured checklist is beneficial to ensure thoroughness. This checklist helps administrators systematically examine various aspects of the MFA system.
- Review of Current MFA Methods: Assess the effectiveness of existing authentication methods (e.g., SMS, authenticator apps, security keys). Are they still appropriate for the level of risk associated with different user roles and data access levels? Consider if there are any methods being underutilized and why.
- User Adoption Rate Analysis: Evaluate the percentage of users successfully enrolled in MFA and identify reasons for low adoption. Are there usability issues or lack of adequate training? Addressing user concerns is vital for effective MFA implementation.
- Risk Assessment and Policy Adjustments: Re-evaluate risk levels for different user groups and adjust MFA requirements accordingly. Higher-risk users might need stronger authentication methods or more frequent authentication prompts.
- Security Auditing and Log Analysis: Review security logs for any unusual MFA-related activity, such as failed login attempts or suspicious authentication requests. This helps identify potential security breaches and vulnerabilities.
- Compliance Requirements: Verify that the MFA policy complies with all relevant industry regulations and internal security standards.
- User Training and Education: Ensure that users receive regular training on MFA best practices and security awareness. This helps improve user adoption and reduce the likelihood of MFA-related security incidents.
- Documentation Updates: Keep all MFA-related documentation updated, including policies, procedures, and troubleshooting guides. This is critical for both users and administrators.
Implementing Robust MFA: Key Considerations
A robust MFA system requires careful planning and execution. This includes selecting appropriate authentication methods based on user needs and risk profiles, ensuring seamless integration with existing systems, and providing comprehensive user training. For example, an organization with a large mobile workforce might prioritize mobile authenticator apps, while an organization handling highly sensitive data might opt for hardware security keys for enhanced security. Careful consideration of the user experience is equally vital to ensure high adoption rates and minimal disruption to workflow. A poorly implemented MFA system can lead to user frustration and ultimately compromise security.
Ending Remarks
Navigating the world of Microsoft Multi-Factor Authentication doesn’t have to be a nightmare. By understanding the common pitfalls, implementing robust security practices, and having a clear troubleshooting plan in place, you can significantly reduce the risk of MFA-related disruptions. Remember, proactive measures are key – regular policy reviews, user training, and a proactive approach to security are your best defenses against MFA headaches. So, ditch the frustration and embrace a smoother, more secure Microsoft experience!


