Cyber attacks 2024: Prepare for a digital warzone. This year isn’t just about another wave of ransomware; it’s about evolving tactics, escalating geopolitical tensions, and the increasingly blurry lines between state-sponsored attacks and everyday cybercrime. We’re diving deep into the predicted trends, the motivations behind the mayhem, and what you need to know to stay ahead of the curve – because in this game, ignorance is not bliss, it’s a vulnerability.
From the rise of AI-powered attacks to the ever-evolving landscape of social engineering, 2024 promises a complex and challenging year for cybersecurity. We’ll unpack the biggest threats, the most effective defenses, and the crucial human element that often makes or breaks a digital siege. Get ready to arm yourself with knowledge; the digital battlefield awaits.
Cyberattack Trends in 2024

Source: deepseas.com
The cyber threat landscape is constantly evolving, making accurate prediction crucial for effective cybersecurity strategies. 2024 promises a continuation of existing trends, alongside the emergence of new and sophisticated attack vectors. Understanding these shifts is paramount for businesses and individuals alike to proactively safeguard their digital assets.
Predicted Rise and Fall of Specific Attack Types
Ransomware attacks, while still prevalent, are predicted to see a slight decrease in sheer volume in 2024. This is not due to a decline in attacker motivation, but rather a shift in tactics. Attackers are increasingly focusing on data exfiltration and extortion, moving beyond simple encryption-based ransomware. Phishing attacks, however, are expected to remain a dominant threat, evolving to become more sophisticated and targeted. The rise of AI-powered phishing tools allows for highly personalized and convincing attacks, making them harder to detect. IoT attacks will continue their upward trajectory, as the number of connected devices continues to explode, creating a vast attack surface. The lack of robust security measures on many IoT devices makes them easy targets for exploitation.
Top Three Emerging Cyber Threats in 2024
Three significant threats are poised to dominate the 2024 cyber landscape:
- AI-powered attacks: Malicious actors are increasingly leveraging artificial intelligence to automate and enhance various attack vectors. This includes creating highly realistic phishing emails, developing sophisticated malware, and automating vulnerability scanning. The impact could be widespread, with AI potentially enabling large-scale, highly targeted attacks that are difficult to detect and defend against. For example, AI could be used to generate personalized phishing emails at scale, bypassing traditional spam filters.
- Supply chain attacks: Targeting vulnerabilities within a company’s supply chain is proving increasingly effective. Attackers compromise a supplier or vendor to gain access to the target organization’s network. The impact can be devastating, allowing attackers to steal sensitive data, deploy ransomware, or disrupt operations. The recent SolarWinds attack serves as a prime example of the devastating consequences of a successful supply chain compromise.
- Deepfakes and disinformation campaigns: The increasing sophistication of deepfake technology poses a significant threat. Deepfakes can be used to create convincing audio or video recordings of individuals, which can be used for blackmail, manipulation, or to spread disinformation. The impact on public trust and social stability could be substantial, as deepfakes can erode confidence in legitimate sources of information. Imagine a deepfake video of a CEO announcing a fraudulent merger, causing significant market disruption.
Comparison of Attack Vectors: 2023 vs. 2024
The following table compares the effectiveness of different attack vectors in 2023 and predicts trends for 2024, along with suggested mitigation strategies:
| Vector | 2023 Effectiveness | 2024 Prediction | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phishing | High; easily bypasses basic security measures | High; increasing sophistication through AI | Advanced email security, employee training, multi-factor authentication |
| Ransomware | Very High; significant financial and operational impact | High; shift towards data exfiltration and extortion | Regular backups, robust security protocols, incident response planning |
| Exploiting Software Vulnerabilities | High; successful if patches are not applied promptly | High; increasing automation through AI-powered tools | Patch management, vulnerability scanning, penetration testing |
| IoT Attacks | Increasing; many devices lack basic security | Very High; expanding attack surface due to increased connectivity | Secure device configurations, network segmentation, IoT security solutions |
Motivations Behind Cyberattacks in 2024
The digital landscape of 2024 presents a complex tapestry of motivations driving cyberattacks. Understanding these diverse incentives is crucial for effective cybersecurity strategies. From nation-states vying for geopolitical advantage to individual criminals seeking financial gain, the spectrum of actors and their goals is constantly evolving. This section will delve into the key drivers behind the increasing frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks.
State-Sponsored Cyber Warfare: Evolving Motivations
State-sponsored cyberattacks are no longer solely focused on espionage. While intelligence gathering remains a primary goal, the motivations are broadening. We’re seeing an increase in attacks aimed at disrupting critical infrastructure, influencing elections, and undermining the stability of rival nations. For example, the potential for crippling a nation’s power grid or manipulating financial markets through cyberattacks is a powerful tool in modern geopolitical conflict. These actions aim not just to steal information but to inflict real-world damage and exert political pressure. The sophistication of these attacks is also increasing, with state-sponsored groups utilizing advanced persistent threats (APTs) and zero-day exploits to maintain a persistent presence within target systems. This allows for long-term data exfiltration and the ability to launch attacks at opportune moments.
Financial Incentives Driving Cybercriminal Activity
The financial rewards associated with successful cyberattacks are a powerful motivator for criminal organizations. Ransomware attacks, for instance, continue to be highly lucrative, with attackers demanding significant sums of money in exchange for decrypting critical data. The ease of monetizing stolen data through the dark web further fuels this trend. Furthermore, the increasing value of personal data on the black market drives attacks targeting individuals and businesses. Identity theft, credit card fraud, and the sale of personal information for malicious purposes are all profitable activities for cybercriminals. The decentralized nature of cryptocurrency transactions makes it easier for attackers to receive and launder their illicit gains, making it even more difficult to trace and prosecute these actors. A recent example is the Conti ransomware group, which generated millions in ransom payments before being disrupted.
Activist Groups and Hacktivism in the Cyberattack Landscape
Hacktivism, the use of hacking to promote a political or social cause, remains a significant factor in the cyberattack landscape. These attacks, while often less sophisticated than state-sponsored or financially motivated attacks, can still cause significant disruption and draw attention to the activists’ cause. Activists might target organizations or individuals perceived as representing oppression or injustice, aiming to expose vulnerabilities, leak sensitive information, or disrupt operations. The motivations are ideologically driven, seeking to raise awareness and pressure for change. However, the line between legitimate activism and criminal activity can be blurry, particularly when attacks result in data breaches or significant service disruptions. The Anonymous collective is a prime example of a group that has used hacktivism to advance various political and social agendas, although their actions have often drawn criticism for collateral damage and lack of precision.
Vulnerabilities and Exploits in 2024
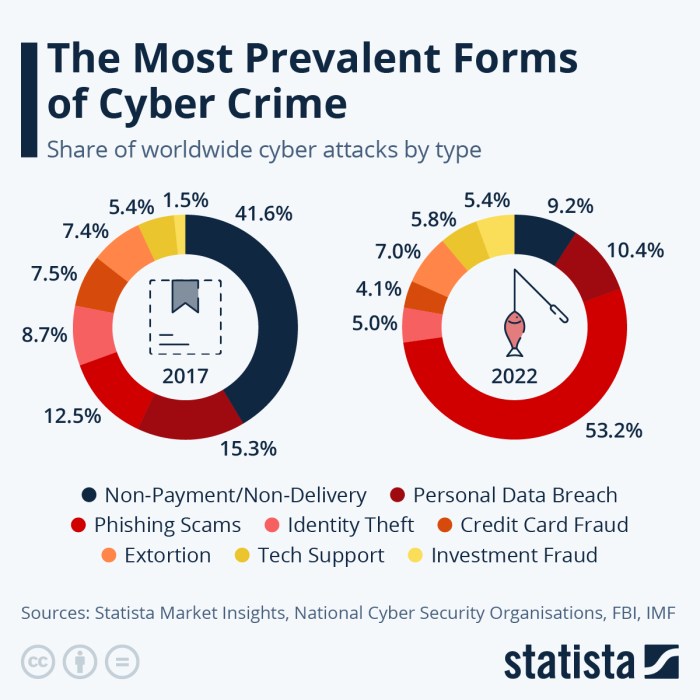
Source: statcdn.com
Predicting the precise vulnerabilities that will dominate the cyberattack landscape in 2024 is akin to predicting the weather a year in advance – there are strong indicators, but unforeseen storms can always brew. However, based on current trends and emerging technologies, we can highlight some likely candidates for exploitation and offer a glimpse into the potential havoc they might wreak. This isn’t a comprehensive list, but rather a spotlight on areas of significant concern.
Critical Software Vulnerabilities Expected to be Exploited in 2024
The convergence of remote work, cloud adoption, and the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand the attack surface for cybercriminals. Three key areas are likely to see increased exploitation in 2024: inadequately secured cloud environments, vulnerabilities in legacy systems, and flaws in widely used open-source software.
Firstly, inadequately secured cloud environments remain a major target. Many organizations rush cloud adoption without fully understanding the security implications. Misconfigurations, lack of proper access controls, and insufficient monitoring create fertile ground for attackers. A recent report by [Insert reputable cybersecurity firm name and report title here] highlighted a significant increase in cloud-based breaches due to simple misconfigurations, such as publicly accessible storage buckets. The ease of exploitation makes this a prime target for both financially motivated actors and state-sponsored groups.
Secondly, vulnerabilities in legacy systems pose a persistent threat. Many businesses rely on older systems that lack modern security updates and patches. These systems often contain known vulnerabilities that are readily available to attackers. The difficulty and cost of upgrading these systems often leads organizations to accept the risk, making them sitting ducks for sophisticated attacks. The infamous NotPetya ransomware attack in 2017, which leveraged a vulnerability in outdated Windows software, serves as a stark reminder of the potential consequences.
Thirdly, flaws in widely used open-source software represent a significant risk. Open-source software is ubiquitous, powering countless applications and services. However, the open nature of this software also means that vulnerabilities are more readily discovered and exploited. The sheer volume of open-source components used in many systems creates a complex web of potential weaknesses. A single vulnerability in a widely used library can cascade through many different applications, creating a massive attack surface.
Examples of Zero-Day Exploits Predicted to be Used in Sophisticated Attacks, Cyber attacks 2024
Zero-day exploits, by their very nature, are difficult to predict. However, we can anticipate that sophisticated attackers will continue to leverage previously unknown vulnerabilities in critical software components, particularly in areas like web browsers, operating systems, and network devices. These exploits are often highly targeted and used in advanced persistent threat (APT) campaigns. For example, we might see an increase in the use of zero-day exploits targeting vulnerabilities in the kernel of widely used operating systems, allowing attackers to gain complete control of a compromised machine. Another likely target would be vulnerabilities in network devices, such as routers and firewalls, allowing attackers to gain unauthorized access to internal networks. These exploits are often custom-developed and extremely valuable on the black market.
Hypothetical Scenario: Exploitation of a Vulnerability Leading to a Data Breach
Imagine a scenario where a small-to-medium-sized business (SMB) uses a popular e-commerce platform that relies on a third-party payment gateway. This payment gateway contains an unknown vulnerability (a zero-day exploit) that allows attackers to inject malicious code into the transaction process. An attacker discovers this vulnerability and crafts a targeted phishing campaign, luring employees into clicking a malicious link. This link executes the malicious code, which exploits the vulnerability in the payment gateway, granting the attacker access to sensitive customer data, including credit card numbers and personal information. The attacker then exfiltrates this data, potentially leading to a massive data breach and significant financial losses for the SMB and its customers. The lack of proactive security measures, such as regular security audits and vulnerability scanning, combined with the unknown vulnerability in the third-party software, creates the perfect storm for a successful attack.
Cybersecurity Defenses for 2024
In 2024, cybersecurity isn’t just about patching vulnerabilities; it’s about proactively anticipating and neutralizing threats. The landscape is shifting rapidly, demanding a more agile and intelligent approach to defense. This requires a blend of advanced technologies, robust security practices, and a proactive mindset focused on threat intelligence.
Proactive Threat Intelligence Gathering and its Application in Mitigating Attacks
Threat intelligence is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity. It involves actively collecting, analyzing, and interpreting information about potential threats to inform defensive strategies. Instead of reacting to attacks after they happen, proactive threat intelligence allows organizations to anticipate attacks, bolster defenses in vulnerable areas, and even disrupt attacks before they can fully materialize. For example, by monitoring dark web forums and threat actor communication channels, organizations can identify potential targets and vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them. This allows for preemptive patching and security hardening, significantly reducing the impact of potential breaches. Furthermore, understanding the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) of specific threat actors enables the development of tailored defenses.
Securing Cloud Infrastructure
The increasing reliance on cloud services necessitates a robust security strategy. The distributed nature of cloud environments presents unique challenges, requiring a layered approach to security.
- Implement strong access controls: Utilize multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users and employ the principle of least privilege, granting users only the access necessary to perform their tasks. This minimizes the damage caused by compromised credentials.
- Regularly patch and update systems: Cloud providers frequently release security updates. Promptly applying these patches is crucial to mitigating known vulnerabilities. Automated patching solutions can streamline this process.
- Utilize cloud security posture management (CSPM) tools: These tools continuously monitor cloud environments for misconfigurations and vulnerabilities, providing alerts and recommendations for remediation. Think of them as your always-on security guard for your cloud infrastructure.
- Employ data loss prevention (DLP) solutions: DLP tools monitor data movement and prevent sensitive information from leaving the cloud environment without authorization. This is critical for protecting intellectual property and confidential data.
- Implement robust monitoring and logging: Continuous monitoring of cloud resources for suspicious activity is essential. Comprehensive logging enables incident response teams to quickly identify and contain security incidents.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning in Enhancing Cybersecurity Defenses
AI and machine learning are revolutionizing cybersecurity by enabling faster and more accurate threat detection and response. Traditional security solutions often struggle to keep pace with the ever-evolving tactics of cybercriminals. AI, however, can analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, identifying patterns and anomalies that might indicate a security breach. For instance, AI can analyze network traffic to identify malicious behavior, such as unusual data transfers or attempts to access unauthorized resources. It can also be used to detect phishing emails and other social engineering attacks by identifying subtle clues that might be missed by human analysts. Furthermore, AI-powered security information and event management (SIEM) systems can correlate security events from multiple sources, providing a more comprehensive view of the security posture of an organization. This allows security teams to respond to threats more effectively and efficiently. Think of AI as your highly skilled and tireless security analyst, constantly monitoring and learning from the data.
The Impact of Geopolitical Events on Cyberattacks in 2024: Cyber Attacks 2024
Geopolitical instability significantly influences the landscape of cyberattacks. International tensions and conflicts often escalate into digital warfare, with nations and non-state actors utilizing cyber capabilities to achieve strategic goals, whether it’s espionage, disruption, or outright sabotage. The increasing interconnectedness of global systems makes critical infrastructure and sensitive data vulnerable to these attacks, highlighting the urgent need for robust cybersecurity measures.
The frequency and nature of cyberattacks are directly correlated with the level of geopolitical tension. Periods of heightened conflict see a surge in attacks, often targeting critical infrastructure, government agencies, and key industries within the opposing nations or their allies. The methods employed can range from sophisticated, state-sponsored attacks to simpler, opportunistic attacks targeting vulnerabilities exposed by the conflict.
The Russo-Ukrainian War’s Cyber Dimension
The ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine has served as a stark example of the intersection of geopolitical conflict and cyber warfare. Both sides, as well as their respective allies and adversaries, have engaged in various cyber operations. These range from disinformation campaigns and website defacements to more sophisticated attacks targeting critical infrastructure, aiming to disrupt essential services and undermine the opponent’s war effort. The conflict has also highlighted the increasing role of private military contractors and other non-state actors in conducting cyberattacks, blurring the lines of responsibility and attribution. For example, the widespread disruption of Ukrainian banking systems in the early days of the invasion, while not definitively attributed, showcased the potential for cyberattacks to significantly impact a nation’s ability to function during a time of conflict. The ongoing use of cyberattacks to target energy grids and communications networks in both countries also demonstrates the destructive potential of cyber warfare in modern conflict.
Tensions in the Taiwan Strait and Their Cyber Implications
The escalating tensions surrounding Taiwan present another significant geopolitical flashpoint with considerable cyber implications. Any escalation of conflict in this region could lead to a significant increase in cyberattacks targeting both Taiwan and mainland China, as well as their respective allies and partners. These attacks could range from targeted attacks on government agencies and critical infrastructure to widespread disinformation campaigns aimed at manipulating public opinion. The high concentration of semiconductor manufacturing in Taiwan makes the island a particularly attractive target for cyber espionage and sabotage, potentially disrupting global supply chains and causing significant economic damage. Moreover, the involvement of various external actors, including the United States, adds another layer of complexity to the potential cyber landscape, with the possibility of proxy cyber conflicts and retaliatory attacks further escalating the situation.
Primary Targets of Cyberattacks in 2024
The increasing interconnectedness of global systems makes a wide range of countries and regions vulnerable to cyberattacks. However, several areas are likely to face a disproportionately high risk in 2024.
Countries and regions directly involved in ongoing or escalating geopolitical conflicts, such as Ukraine, Taiwan, and potentially other nations in Eastern Europe or the Indo-Pacific, are prime targets. Their critical infrastructure, government systems, and key industries are likely to be the focus of both state-sponsored and non-state actor cyberattacks. Furthermore, countries with strong economic ties to these regions, including those in North America and Europe, may also face increased cyber threats due to their proximity and potential for involvement in the conflicts. Finally, countries with significant technological capabilities and intellectual property, such as those in the United States and South Korea, are likely to continue to be targets for cyber espionage and theft of sensitive data. The motivation behind these attacks will vary, ranging from geopolitical advantage and economic gain to simple disruption and demonstration of capabilities.
The Human Element in Cyberattacks 2024
The human element remains the weakest link in any cybersecurity system. Despite increasingly sophisticated technological defenses, the success of many cyberattacks hinges on exploiting human vulnerabilities – our tendencies towards carelessness, trust, and susceptibility to social engineering. 2024 will likely see a continued reliance on these human factors, with attackers refining their techniques to maximize their effectiveness.
Human error contributes significantly to successful cyberattacks in various ways, from clicking on malicious links to failing to update software or adhering to security protocols. These seemingly small oversights can have devastating consequences, providing attackers with easy entry points into systems. The consequences range from data breaches and financial losses to reputational damage and operational disruption. Even highly trained professionals are not immune; fatigue, time pressure, and the sheer volume of daily digital interactions create opportunities for mistakes.
Social Engineering Techniques in 2024
Sophisticated social engineering techniques are predicted to become even more prevalent in 2024. Attackers are constantly innovating, moving beyond simple phishing emails to more personalized and targeted approaches. This includes using AI-powered tools to craft convincing messages tailored to individual victims, exploiting their personal information and social connections to increase the likelihood of success. The effectiveness of these methods relies on manipulating human psychology, playing on emotions like fear, urgency, or curiosity to trick victims into revealing sensitive information or performing actions that compromise security. For example, we might see a rise in highly targeted attacks against specific individuals within organizations, leveraging their professional roles and responsibilities to gain access to critical systems.
A Phishing Attack Scenario
Imagine Sarah, a mid-level manager at a financial institution. She receives an email seemingly from her CEO, requesting immediate action on a supposedly urgent financial transaction. The email is perfectly formatted, using the CEO’s official email address and even incorporating details from recent company meetings. The email contains a link to a seemingly legitimate document requiring her immediate attention. Sarah, under pressure to meet deadlines, clicks the link, unknowingly downloading malware onto her computer. This malware grants the attacker remote access to her system, allowing them to steal sensitive financial data and potentially access the company’s internal network. The impact could be catastrophic, leading to significant financial losses, reputational damage for the company, and legal repercussions for Sarah and the organization. The attacker’s success hinged entirely on Sarah’s trust and the urgency created by the carefully crafted email. This scenario illustrates how seemingly minor human errors can have major consequences in the context of sophisticated cyberattacks.
Cybersecurity Legislation and Regulations in 2024
The landscape of cybersecurity legislation is constantly evolving, driven by increasingly sophisticated cyber threats and a growing awareness of the potential damage they can inflict. 2024 sees a continuation of this trend, with new regulations coming into force and existing ones being updated to better address emerging challenges. This impacts organizations significantly, demanding proactive adaptation and robust compliance strategies.
The impact of these changes is far-reaching, affecting organizations of all sizes and across various sectors. From stricter data protection laws to mandatory breach notification requirements, the regulatory burden is increasing, requiring significant investment in both technology and expertise. Failure to comply can lead to hefty fines, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust.
The Impact of New and Updated Cybersecurity Legislation on Organizations
New cybersecurity legislation and updated regulations are forcing organizations to re-evaluate their security postures. The increased focus on data privacy, for instance, necessitates the implementation of more stringent data protection measures, including robust encryption, access controls, and data loss prevention (DLP) strategies. Regulations like the EU’s Digital Services Act (DSA) and the Digital Markets Act (DMA) are pushing organizations to take responsibility for the security of their online services and the data they handle. Compliance requires a shift from reactive to proactive security management, prioritizing risk assessment, vulnerability management, and incident response planning. This often involves significant investment in new technologies, training, and personnel. For example, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and similar state-level laws have driven organizations to develop comprehensive privacy programs, including processes for handling consumer data requests and responding to data breaches.
Challenges in Complying with Evolving Regulations
Staying compliant with the rapidly evolving cybersecurity regulatory landscape presents several significant challenges. The sheer volume and complexity of regulations across different jurisdictions can be overwhelming, requiring specialized expertise to navigate. Keeping up with updates and amendments is also a constant challenge, demanding continuous monitoring and adaptation of security practices. Furthermore, many organizations struggle with resource constraints, lacking the budget, personnel, or technical capabilities to implement the necessary security controls effectively. Another challenge is integrating new security measures into existing systems and workflows without disrupting operations. This requires careful planning, testing, and change management. Finally, the ever-changing threat landscape necessitates continuous adaptation, meaning that achieving complete compliance is an ongoing process rather than a one-time achievement.
Best Practices for Ensuring Compliance with Cybersecurity Legislation
Organizations can implement several best practices to ensure compliance with relevant legislation. First, conducting regular risk assessments is crucial to identify vulnerabilities and prioritize mitigation efforts. This involves evaluating the organization’s assets, threats, and vulnerabilities, and determining the likelihood and impact of potential incidents. Second, developing and implementing a comprehensive cybersecurity policy that Artikels the organization’s security goals, responsibilities, and procedures is essential. This policy should cover all aspects of cybersecurity, including data protection, incident response, and employee training. Third, investing in robust security technologies, such as intrusion detection systems (IDS), firewalls, and endpoint protection solutions, is vital to protect against cyber threats. Fourth, implementing employee training programs to raise awareness about cybersecurity risks and best practices is crucial to prevent human error, a major factor in many cyberattacks. Fifth, maintaining thorough documentation of security policies, procedures, and incidents is essential for demonstrating compliance to auditors and regulators. Finally, engaging with external cybersecurity experts for regular audits and assessments can provide valuable insights and ensure that the organization’s security posture aligns with evolving regulations. Regular penetration testing and vulnerability scans also form a crucial part of this ongoing process.
Conclusive Thoughts
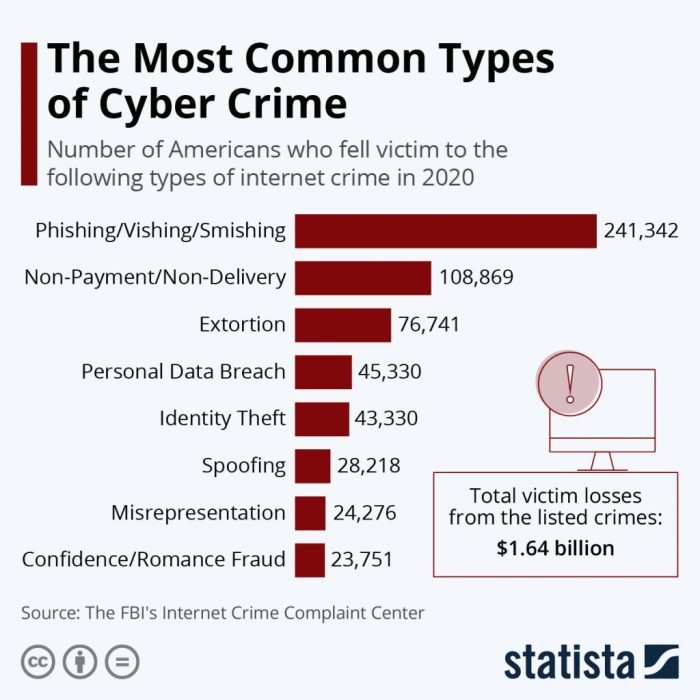
Source: kratikal.com
So, 2024’s cyber threat landscape? It’s a wild west of sophisticated attacks, geopolitical maneuvering, and the constant cat-and-mouse game between hackers and defenders. While the future holds uncertainty, one thing’s clear: proactive security measures, a keen understanding of evolving threats, and a healthy dose of digital skepticism are your best weapons. Stay vigilant, stay informed, and stay secure – because in the digital age, survival is a constant battle.


