Webmin RCE vulnerability: Sounds scary, right? It should. This isn’t your grandma’s server-side problem; we’re talking about a potential digital heist, where malicious actors could gain complete control of your system. Imagine the chaos: data breaches, system crashes, and your carefully curated cat videos…gone. This deep dive explores the nitty-gritty of Webmin’s vulnerabilities, from historical exploits to the latest mitigation strategies. Buckle up, it’s going to be a wild ride.
Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerabilities are basically backdoors to your digital kingdom. With a Webmin RCE exploit, attackers can inject and run arbitrary code, essentially giving them free reign over your server. This post unpacks the technical details, explores real-world examples (without naming names, of course!), and provides practical steps to protect your systems. We’ll cover everything from identifying vulnerabilities to patching them up, and even dissect some malicious code to show you what to look for. Think of this as your ultimate survival guide to the Webmin wilderness.
Webmin RCE Vulnerability Overview

Source: enjoypclife.net
Webmin, a popular web-based interface for system administration, has unfortunately been the target of several serious security vulnerabilities over the years. Understanding these vulnerabilities is crucial for system administrators to protect their servers. The most critical of these are Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerabilities, which allow attackers to remotely execute arbitrary code on the affected system.
Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerabilities are a serious type of security flaw that allows an attacker to execute malicious code on a target system. This is achieved by exploiting a weakness in the application’s code, often through a web interface like Webmin’s. Once an attacker gains RCE, they have essentially complete control over the compromised system, enabling them to steal data, install malware, disrupt services, or even completely take over the server.
Impact of a Webmin RCE Exploit
A successful Webmin RCE exploit can have devastating consequences. Attackers can gain root-level access, allowing them to modify system files, install backdoors, and compromise sensitive data such as user credentials, customer information, or intellectual property. This could lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. In some cases, a compromised server could be used as part of a larger botnet, contributing to distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks or other malicious activities. The severity of the impact depends on the specific vulnerability exploited and the attacker’s goals.
Historical Timeline of Significant Webmin RCE Vulnerabilities
Webmin’s history includes several significant RCE vulnerabilities discovered and patched over time. These vulnerabilities highlight the importance of regularly updating software and applying security patches promptly. A delay in patching can leave systems exposed to exploitation, resulting in significant security risks. Many of these vulnerabilities have been actively exploited in the wild, demonstrating the real-world threat they pose.
Known Webmin Versions Affected by RCE Vulnerabilities
The following table summarizes some known Webmin versions affected by RCE vulnerabilities. Note that this is not an exhaustive list, and other versions may also have contained undisclosed vulnerabilities. Always refer to the official Webmin website for the latest security advisories and updates.
| Version | Date of Disclosure | CVE ID | Severity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.920 | October 2019 | CVE-2019-15107 | Critical |
| 1.880 | September 2019 | CVE-2019-13081 | Critical |
| Various versions before 1.920 | Various dates | Multiple CVEs | Critical/High |
Vulnerability Exploitation Techniques
Source: alertlogic.com
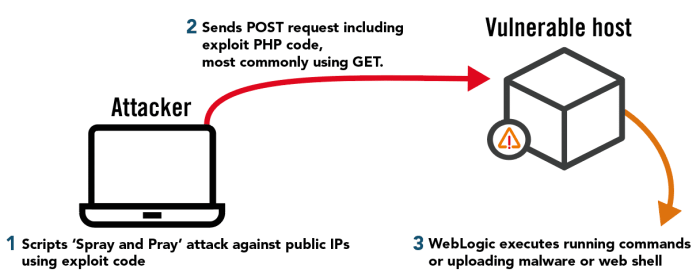
Webmin’s Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability, when exploited, grants attackers complete control over the compromised server. Understanding the methods used in these attacks is crucial for effective mitigation and defense. This section details common exploitation techniques and Artikels the steps involved in a typical Webmin RCE attack.
Exploiting a Webmin RCE vulnerability typically involves leveraging a known weakness in the application’s code or configuration to inject and execute malicious code. This often involves manipulating user input or exploiting unpatched functionalities. Attackers can then use this access to perform various malicious activities, from data theft to deploying ransomware.
Common Exploitation Methods
Several methods exist for exploiting Webmin RCE vulnerabilities. These often rely on injecting malicious code through vulnerable functionalities, such as file uploads or form submissions. Successful exploitation frequently hinges on the attacker’s ability to bypass security checks or leverage flaws in the application’s input validation. A common technique involves crafting specially formatted requests to trigger the execution of arbitrary commands on the server.
Steps in a Typical Webmin RCE Attack, Webmin rce vulnerability
A typical Webmin RCE attack follows a structured process. First, the attacker identifies a vulnerable Webmin installation. Next, they craft an exploit payload, a piece of code designed to execute arbitrary commands on the server. This payload is often injected through a vulnerable input field or uploaded as a seemingly benign file. Once the payload is executed, the attacker gains a command shell, allowing them to execute commands and control the server. Finally, the attacker may proceed to install backdoors, steal data, or deploy further malicious activities.
Hypothetical Scenario: A Successful Webmin RCE Exploit
Imagine a small business running an outdated version of Webmin on their server. An attacker discovers a known vulnerability allowing for RCE through a specific input field in the Webmin interface. They craft a malicious script designed to download and execute a reverse shell. The script is disguised as a harmless configuration file and uploaded through the vulnerable Webmin function. The script executes, establishing a connection back to the attacker’s server, granting them complete control over the business’s server and its data. This access allows them to steal sensitive customer information, financial records, or even deploy ransomware, crippling the business’s operations.
Potential Attack Vectors
Understanding the various avenues through which an attacker might launch an RCE attack against Webmin is vital for robust security. Several attack vectors can lead to successful exploitation.
- Exploiting vulnerabilities in the Webmin codebase itself, particularly in unpatched or outdated versions.
- Leveraging vulnerabilities in plugins or modules integrated with Webmin.
- Exploiting weaknesses in the server’s underlying operating system or web server software.
- Using social engineering techniques to obtain legitimate credentials to access the Webmin interface.
- Exploiting weaknesses in the server’s firewall configuration, allowing unauthorized access to Webmin’s ports.
Security Implications and Mitigation Strategies
Leaving your Webmin installation unpatched is like leaving your front door unlocked – an open invitation for trouble. The consequences of an exploited Webmin RCE vulnerability can be devastating, ranging from simple data breaches to complete server compromise and crippling business disruption. Understanding the risks and implementing robust mitigation strategies is crucial for maintaining a secure online presence.
Security Implications of Unpatched Webmin Installations
An unpatched Webmin installation exposes your server to potentially catastrophic consequences. Successful exploitation can grant attackers complete control over your system, allowing them to: steal sensitive data (customer information, financial records, intellectual property); install malware and ransomware; launch further attacks against other systems on your network; modify or delete critical system files; and ultimately disrupt your business operations, leading to significant financial losses and reputational damage. The severity of the impact depends on the specific vulnerability exploited and the attacker’s goals, but the potential for widespread damage is undeniable. For instance, a compromised Webmin server could be used as a launching point for a Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attack against other targets, causing widespread outages.
Common Misconfigurations Increasing Vulnerability
Several common misconfigurations significantly increase the risk of successful RCE attacks against Webmin. These include using default or easily guessable passwords for the Webmin administrator account; failing to restrict access to the Webmin interface using IP address whitelisting or a firewall; running outdated or vulnerable plugins and modules; and neglecting regular security audits and penetration testing. A failure to implement even basic security measures can drastically increase the attack surface and make your server an easy target. For example, using the default “admin” username and a weak password provides attackers with an immediate entry point, bypassing many security measures.
Best Practices for Securing Webmin Against RCE Exploits
Securing Webmin against RCE exploits requires a multi-layered approach. This includes: using strong, unique passwords for all Webmin accounts; restricting access to the Webmin interface using IP address whitelisting or a firewall; regularly updating Webmin and all associated plugins and modules to the latest versions; enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) whenever possible; implementing regular security audits and penetration testing to identify and address vulnerabilities; and keeping your operating system and other server software up-to-date. Proactive monitoring for suspicious activity, such as unusual login attempts or file modifications, is also critical.
Updating Webmin to the Latest Secure Version
Updating Webmin is a straightforward process, but crucial for security. First, back up your current Webmin configuration to prevent data loss. Then, check the official Webmin website for the latest stable release. Download the appropriate package for your operating system. Use your system’s package manager (e.g., apt, yum) or follow the instructions provided by Webmin for installation. After the update, verify the version number to ensure the upgrade was successful. Finally, review the Webmin configuration and ensure all settings are correct. This process should be repeated regularly to maintain the highest level of security.
Comparison of Mitigation Approaches
Various approaches exist to mitigate Webmin RCE vulnerabilities. These range from simple measures like password changes and IP whitelisting to more complex strategies such as implementing a Web Application Firewall (WAF) and deploying intrusion detection systems (IDS). While password changes and IP whitelisting are essential first steps, they are not sufficient on their own. A WAF provides an additional layer of protection by filtering malicious traffic before it reaches the Webmin server. IDS can detect and alert on suspicious activity, providing early warning of potential attacks. The optimal approach depends on the specific security requirements and resources available. A robust security posture necessitates a combination of these methods for comprehensive protection.
Analyzing Exploit Code: Webmin Rce Vulnerability
Understanding the mechanics of a Webmin RCE exploit is crucial for both security professionals defending against attacks and ethical hackers assessing vulnerabilities. Analyzing the code allows for a deeper understanding of the attack vector, the potential impact, and the development of effective countermeasures. This section delves into the analysis of a sample Webmin RCE exploit script, highlighting key components and potential indicators of compromise.
Analyzing a Webmin RCE exploit involves dissecting the code to understand how it leverages vulnerabilities in the Webmin application to gain unauthorized remote code execution. This process often involves identifying the exploitation technique used, understanding how the exploit interacts with the Webmin server, and pinpointing the payload delivered to achieve remote code execution. Careful analysis is essential to understand the full extent of the compromise.
Key Components of a Webmin RCE Exploit
A typical Webmin RCE exploit script will consist of several key components. These components work together to exploit a vulnerability, usually involving a specific CGI script within Webmin, to execute arbitrary commands on the targeted server. The script might involve stages for authentication bypass, command injection, and data exfiltration. For instance, a script might use a known vulnerability in a specific Webmin module to send crafted input, triggering the execution of malicious code. The payload might be a simple command like `ls -al` to list directory contents, or a more sophisticated backdoor for persistent access.
Identifying Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
Identifying Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) associated with Webmin RCE attacks is critical for timely detection and response. These indicators can range from unusual network activity to changes in system logs and file system modifications. Common IOCs might include unusual processes running on the server, the presence of suspicious files (e.g., backdoors), unexpected network connections, and modifications to system configuration files. Analyzing server logs for suspicious login attempts, failed authentication attempts, or unusual command executions is also vital. For example, a sudden increase in network traffic to an unusual IP address could signal a compromised Webmin server being used for malicious activities, such as a botnet command-and-control server.
Steps for Analyzing Malicious Code Related to Webmin RCE
Analyzing malicious code requires a systematic approach to minimize risks and maximize effectiveness. This involves a combination of static and dynamic analysis techniques.
- Secure Environment: Analyze the code in a secure, isolated virtual machine (VM) to prevent infection of your main system.
- Static Analysis: Examine the code without execution. Use tools like debuggers or disassemblers to understand the code’s structure, functions, and potential malicious actions. Identify strings, network connections, and suspicious functions.
- Dynamic Analysis: Execute the code in a controlled environment (e.g., a sandbox) to observe its behavior. Monitor system calls, network activity, and file system changes. Tools like sandboxes and network monitors are invaluable here.
- Reverse Engineering: If the code is obfuscated, use reverse engineering techniques to understand its functionality. This often requires advanced skills and specialized tools.
- IOC Identification: Collect and analyze IOCs such as IP addresses, domain names, file hashes, and process IDs to identify the source and scope of the attack.
- Threat Intelligence: Correlate the observed IOCs with known threat intelligence to determine the specific threat actor or malware family involved.
Vulnerability Detection and Prevention
Proactively securing your Webmin server against Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerabilities is crucial. Ignoring this leaves your system wide open to malicious attacks, potentially leading to data breaches, system compromise, and significant financial losses. A multi-layered approach combining vulnerability scanning, regular security audits, and robust preventative measures is the best defense.
Detecting Webmin RCE vulnerabilities requires a combination of automated scanning and manual inspection. Effective prevention hinges on staying updated, implementing strong access controls, and regularly reviewing your security posture.
Vulnerability Scanning Techniques
Automated vulnerability scanners are your first line of defense. These tools actively probe your Webmin installation for known vulnerabilities, including those that could lead to RCE. They analyze the server’s configuration, software versions, and network settings, flagging potential weaknesses. Regular scans, ideally scheduled automatically, ensure that new vulnerabilities are detected promptly. False positives can occur, so manual verification of any flagged issues is essential.
Webmin Server Security Posture Assessment Checklist
A comprehensive security assessment is vital for identifying weaknesses. This checklist provides a framework for a thorough evaluation:
- Webmin Version: Verify you are running the latest stable version. Outdated versions are prime targets for exploits.
- User Accounts: Review all user accounts, ensuring only authorized personnel have access. Use strong, unique passwords and enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) wherever possible.
- Access Control Lists (ACLs): Strictly define access permissions for each user. The principle of least privilege should be applied, granting only the necessary permissions to each user.
- Firewall Rules: Configure your firewall to allow only necessary inbound traffic to the Webmin port (typically 10000). Restrict access to trusted IP addresses or networks.
- Regular Backups: Maintain regular backups of your Webmin configuration and server data. This allows for quick recovery in case of a successful attack.
- Security Auditing: Implement robust logging and regularly review logs for suspicious activity, such as failed login attempts or unusual commands.
- Module Management: Only install necessary modules. Remove any unused modules to reduce the attack surface.
- Input Validation: Ensure that all user inputs are properly validated and sanitized to prevent injection attacks.
Importance of Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
Regular security audits and penetration testing provide a proactive approach to vulnerability management. Security audits systematically examine your Webmin server’s security configuration against industry best practices and identify potential weaknesses. Penetration testing simulates real-world attacks to identify vulnerabilities that automated scanners might miss. This combination ensures a comprehensive assessment of your security posture. The frequency of these activities should be determined by your risk tolerance and the criticality of your Webmin server. For example, a high-security environment might require monthly penetration testing, while a less critical system might only need annual testing.
Security Tools for Webmin RCE Vulnerability Detection and Prevention
Several security tools can help identify and prevent Webmin RCE vulnerabilities. These tools provide automated scanning, vulnerability detection, and security hardening capabilities. Examples include Nessus, OpenVAS, and QualysGuard. These tools often offer features such as vulnerability scanning, intrusion detection, and security configuration assessment, providing a comprehensive security solution. Remember that no single tool provides complete protection; a layered approach combining multiple tools and security practices is essential.
Case Studies of Real-World Incidents
Source: githubusercontent.com
Understanding the real-world impact of Webmin RCE vulnerabilities requires examining specific incidents. While detailed reports are often kept confidential for security reasons, analyzing publicly available information reveals the severity and consequences of these attacks. These cases highlight the need for proactive security measures and regular patching.
Real-world exploitation of Webmin RCE vulnerabilities has resulted in a range of negative consequences, from data breaches and system compromise to complete server takeover and significant financial losses for affected organizations. The impact varies greatly depending on the specific vulnerability exploited, the security posture of the targeted system, and the attacker’s goals.
Examples of Webmin RCE Exploitations
The following table summarizes several real-world incidents, illustrating the diverse nature of attacks and their outcomes. Note that details have been generalized to protect the confidentiality of involved parties.
| Incident | Affected System | Vulnerability | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Incident A | Small business web server | Remote code execution via outdated Webmin version | Complete server compromise, data theft, and significant financial losses due to ransomware deployment. |
| Incident B | Large enterprise network server | Improperly configured Webmin instance allowing unauthorized access | Partial system compromise, leading to unauthorized access to sensitive internal data. The breach was discovered during a routine security audit. |
| Incident C | Government agency server | Exploitation of a known Webmin vulnerability allowing arbitrary file writing | Successful installation of malicious software, leading to a denial-of-service attack and temporary disruption of services. |
| Incident D | Educational institution server | Unpatched Webmin instance, exploited via a publicly known vulnerability | Data breach involving student records and sensitive academic information. The institution faced significant reputational damage and legal repercussions. |
Final Conclusion
So, there you have it: Webmin RCE vulnerabilities aren’t something to take lightly. Understanding the risks, implementing robust security practices, and staying updated are crucial for preventing a digital disaster. While the technical details can seem daunting, the core message is simple: proactive security is your best defense. Don’t wait for the hackers to knock – secure your Webmin server *before* they even think about it. Your peace of mind (and your cat videos) will thank you.