Thomas Cook hit by cyber attack: The headline alone screams drama, right? This isn’t just another tech glitch; we’re diving deep into the chaos, the fallout, and the long-term consequences for a travel giant blindsided by digital bandits. From booking systems grinding to a halt to the chilling reality of customer data breaches, we unpack the full impact of this cyberattack, revealing the vulnerabilities within a seemingly impenetrable industry.
We’ll explore the nature of the attack itself – was it ransomware, a sophisticated data breach, or something else entirely? We’ll examine Thomas Cook’s response, dissecting their communication strategy and the resources thrown into damage control. But more importantly, we’ll analyze the lasting scars: the reputational damage, the financial hit, and the crucial lessons learned (or perhaps not learned) that could shape the future of cybersecurity in the travel industry.
The Immediate Impact of the Cyberattack

Source: particlenews.com
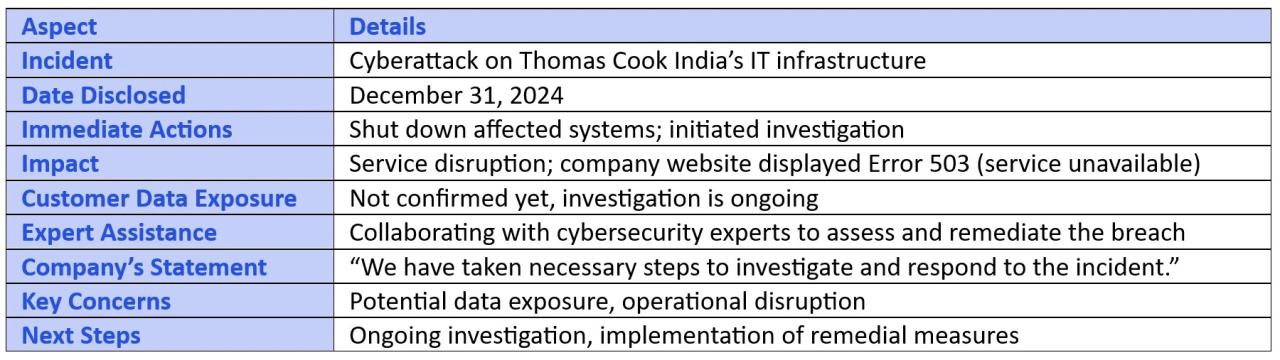
The cyberattack on Thomas Cook wasn’t just a headline; it was a seismic event that sent shockwaves through the travel industry and left a trail of disruption and financial fallout in its wake. The immediate impact was swift and brutal, highlighting the vulnerability of even established companies to sophisticated digital attacks.
The attack crippled core operational systems, instantly impacting the company’s ability to function effectively. This wasn’t a minor glitch; it was a full-blown crisis that brought significant parts of the business to a standstill.
Services Affected by the Cyberattack, Thomas cook hit by cyber attack
The cyberattack severely compromised several crucial systems. The booking systems, the lifeblood of any travel agency, were rendered unusable, preventing new bookings and causing significant delays in processing existing ones. Furthermore, the customer database, containing sensitive personal and financial information, was also targeted, raising serious concerns about data breaches and potential identity theft. Internal communication systems were also disrupted, hindering the company’s ability to coordinate its response effectively. The ripple effect was immediate and widespread, affecting every aspect of the business, from customer service to financial operations.
Financial Consequences of the Cyberattack
The immediate financial consequences were substantial and multifaceted. The inability to process new bookings led to a significant loss of revenue. The cost of investigating the attack, implementing security measures, and managing the ensuing PR crisis added further financial strain. Legal fees, potential compensation claims from affected customers, and the overall damage to the company’s reputation all contributed to a substantial financial burden. While the exact figures weren’t immediately released, it’s clear the attack inflicted a severe blow to Thomas Cook’s already fragile financial position, potentially accelerating its eventual collapse.
Customer Reactions and Concerns
The cyberattack caused widespread anxiety and frustration among Thomas Cook’s customers. The uncertainty surrounding the security of their personal data and the disruption to their travel plans led to a wave of complaints and concerns. The following table summarizes the reported customer reactions and their subsequent actions and outcomes:
| Customer Segment | Primary Concern | Action Taken | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customers with upcoming bookings | Cancellation of flights/hotels, loss of prepaid money | Contacted customer service, sought refunds | Varied; some received refunds, others faced significant delays |
| Customers with existing bookings | Access to booking details, potential data breach | Requested confirmation of booking details, monitored credit reports | Many received confirmation, but concerns about data security remained |
| Customers with personal data in the database | Identity theft, fraudulent activity | Monitored bank accounts and credit reports, contacted credit agencies | The long-term impact remains to be seen, but the risk of identity theft was significant |
| Potential future customers | Concerns about data security, company reliability | Avoided booking with Thomas Cook, chose alternative providers | Loss of future business for Thomas Cook |
The Nature of the Cyberattack

Source: toiimg.com
The Thomas Cook cyberattack, while shrouded in some secrecy due to the sensitive nature of the incident and subsequent investigations, points towards a sophisticated, multi-stage operation likely involving a combination of techniques rather than a single, easily categorized attack. While the exact details remain undisclosed, piecing together available information suggests a complex scenario impacting various aspects of the company’s operations.
The attack wasn’t simply a single ransomware deployment or a straightforward data breach. Instead, evidence suggests a more insidious approach designed to disrupt operations and potentially exfiltrate sensitive data over a period of time. The lack of immediate public statements regarding the type of malware or attack vector employed points to a deliberate strategy to minimize immediate damage and allow for a more thorough investigation. The subsequent bankruptcy filing, however, strongly suggests the attack had a significant impact on the company’s ability to function.
Attack Type and Vector
The nature of the attack likely involved multiple stages. Initial access might have been gained through phishing emails targeting employees, a common tactic for gaining initial footholds in corporate networks. Once inside, the attackers likely employed lateral movement techniques to gain access to sensitive systems containing customer data, financial records, and operational information. The significant disruption to operations suggests the attackers may have used some form of ransomware or deployed malware designed to cripple critical systems, hindering Thomas Cook’s ability to process bookings, manage flights, and handle customer inquiries. The absence of a public ransomware claim doesn’t rule out its involvement; attackers often prefer to negotiate quietly for financial gain rather than publicizing their actions. The significant operational disruption points towards the likely deployment of malware designed to disrupt key business functions rather than simply encrypting data.
Attack Sophistication and Methods
The attackers demonstrated a level of sophistication in their approach. They likely used advanced techniques to avoid detection, potentially employing tools to evade security software and move laterally within the network undetected. The lack of immediate detection suggests the attackers were skilled in maintaining persistence and avoiding detection by security systems. They may have used techniques like living off the land (LotL) attacks, leveraging legitimate system tools to avoid raising suspicion. The extended period before discovery further indicates a well-planned and executed attack. The attackers likely conducted reconnaissance before launching their attack, identifying vulnerabilities and critical systems to target for maximum impact.
Timeline of Events
While a precise timeline remains unavailable, we can construct a plausible sequence of events based on available information. The attack likely began several weeks or even months before its discovery. The attackers gained initial access, possibly through phishing, and then moved laterally within the network. They deployed malware designed to disrupt operations and potentially exfiltrate data. The attack went undetected for a significant period, potentially due to weaknesses in Thomas Cook’s security infrastructure or the sophistication of the attacker’s methods. The discovery of the attack likely triggered a rapid response, including attempts to contain the damage and initiate forensic investigations. The severity of the situation ultimately contributed to the company’s collapse.
Thomas Cook’s Response to the Attack
Thomas Cook’s response to the 2018 cyberattack, while ultimately unsuccessful in preventing the company’s collapse, provides a case study in the complexities of incident response for a large multinational corporation. Their actions, or lack thereof, in several key areas highlight the critical balance between immediate containment, effective communication, and resource allocation during such crises. The speed and effectiveness of their response were arguably crucial factors in the subsequent fallout.
The company immediately initiated an incident response plan, engaging internal IT security teams and external cybersecurity specialists. This involved isolating affected systems to prevent further data breaches, conducting a thorough forensic investigation to determine the extent of the compromise, and implementing enhanced security measures to mitigate future risks. While specific details about the technical steps taken remain confidential, reports suggest a focus on patching vulnerabilities, strengthening network defenses, and implementing more robust monitoring systems. The immediate priority was to secure customer data and prevent further exploitation.
Containment and Investigation Efforts
The investigation into the cyberattack involved a multi-faceted approach. This included analyzing system logs, network traffic, and compromised data to identify the attackers’ methods, objectives, and the extent of the data breach. Thomas Cook collaborated with law enforcement agencies and cybersecurity firms to leverage their expertise and resources. The goal was not only to contain the immediate threat but also to understand the attack’s root cause and prevent similar incidents in the future. The scale of the investigation would have necessitated significant human and technological resources, potentially involving hundreds of hours of work from specialists across multiple disciplines.
Communication Strategy
Thomas Cook’s communication strategy following the attack was a mixed bag. While they acknowledged the incident relatively quickly, the initial statements lacked specifics, potentially fueling speculation and anxiety among customers and stakeholders. The company struggled to balance transparency with the need to protect ongoing investigations and avoid further panic. Communication was primarily through press releases and updates on their website, targeting a broad audience rather than offering personalized support to individual customers affected. This approach, while understandable given the scale of the situation, may have contributed to the negative perception of their handling of the crisis. A more proactive, personalized communication approach, perhaps utilizing targeted email campaigns and social media engagement, might have mitigated some of the negative impact.
Resource Allocation
The resources dedicated to the incident response likely encompassed significant financial and human capital. The costs included hiring external cybersecurity experts, forensic investigators, legal counsel, and public relations professionals. Internal IT teams also dedicated considerable time and effort to the investigation, remediation, and system recovery. While precise figures remain undisclosed, the overall expense would have been substantial, potentially impacting the company’s already fragile financial position. The allocation of these resources, particularly the prioritization of certain tasks over others, likely played a significant role in shaping the outcome of the incident and the company’s overall response.
Comparison with Similar Incidents
Comparing Thomas Cook’s response to similar incidents in other travel companies reveals both similarities and differences. Many travel companies have experienced data breaches, and their responses have generally involved similar steps: incident investigation, containment, customer notification, and enhanced security measures. However, the scale and impact of the Thomas Cook breach, coupled with the company’s pre-existing financial vulnerabilities, distinguished it from other incidents. Unlike some companies that successfully weathered similar storms, Thomas Cook’s response may have been hampered by internal weaknesses and a lack of sufficient resources to effectively address the multifaceted challenges presented by the cyberattack. The absence of a robust, well-rehearsed incident response plan may have also contributed to the negative outcome.
The Long-Term Effects on Thomas Cook
The cyberattack on Thomas Cook wasn’t just a temporary setback; it left deep scars on the company’s reputation and financial health, significantly impacting its long-term viability. The incident served as a stark reminder of the devastating consequences of inadequate cybersecurity measures in a highly sensitive industry like travel. The ripple effects extended far beyond the immediate disruption, shaping the company’s future in profound ways.
The reputational damage inflicted by the cyberattack was considerable. Customers lost trust, questioning the company’s ability to safeguard their personal and financial information. This erosion of confidence directly impacted bookings, leading to a decline in revenue and market share. The negative media coverage further amplified the damage, painting a picture of a company struggling with both operational and security challenges. This negative perception lingered long after the immediate crisis subsided, hindering recovery efforts.
Long-Term Financial Implications
The financial repercussions of the cyberattack were multifaceted. The direct costs included expenses related to incident response, data recovery, legal fees, and regulatory fines. However, the indirect costs were arguably more significant. The loss of customer trust resulted in decreased bookings and revenue, impacting profitability and potentially hindering future investments. The company might have also faced increased insurance premiums and difficulties securing future funding due to the perceived heightened risk. The long-term financial instability ultimately contributed to the company’s eventual collapse, demonstrating the severe financial ramifications of a major cybersecurity breach.
Changes to Thomas Cook’s Security Infrastructure
Following the cyberattack, Thomas Cook was compelled to overhaul its security infrastructure. This involved implementing more robust authentication systems, enhancing data encryption protocols, and strengthening its network security. Employee training programs focused on cybersecurity awareness were also likely implemented. While the specific details of these changes may not be publicly available due to competitive and security reasons, it’s reasonable to assume a significant investment was made to improve the company’s overall cybersecurity posture. However, these improvements came too late to save the company from its ultimate demise.
Hypothetical Plan for Improving Cybersecurity Protocols in the Travel Industry
The Thomas Cook case highlights the critical need for robust cybersecurity protocols within the travel industry. A comprehensive plan to improve industry-wide security should include:
A proactive approach is essential to mitigate the risks associated with cyberattacks. This involves a multi-pronged strategy focusing on prevention, detection, and response.
- Mandatory Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Regular independent security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses before they can be exploited.
- Enhanced Employee Training: Comprehensive cybersecurity awareness training for all employees, focusing on phishing scams, social engineering, and password security.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implementing MFA for all systems and applications to add an extra layer of security and reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
- Data Encryption and Loss Prevention: Encrypting sensitive customer data both in transit and at rest to protect against data breaches. Implement robust data loss prevention (DLP) measures to prevent unauthorized data exfiltration.
- Incident Response Plan Development: Every travel company should have a detailed incident response plan that Artikels procedures for handling a cyberattack, including communication protocols and data recovery strategies.
- Collaboration and Information Sharing: Fostering collaboration between travel companies and cybersecurity experts to share threat intelligence and best practices.
- Investment in Advanced Security Technologies: Utilizing advanced security technologies such as intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), security information and event management (SIEM) systems, and threat intelligence platforms.
Legal and Regulatory Implications
The Thomas Cook cyberattack didn’t just disrupt travel plans; it triggered a cascade of legal and regulatory ramifications, highlighting the significant liabilities companies face in the digital age. The fallout extended beyond immediate customer service issues, impacting the company’s reputation and financial stability in profound ways. Understanding the legal landscape surrounding data breaches is crucial for any business handling sensitive customer information.
The potential legal liabilities for Thomas Cook stemmed from various data protection regulations and contractual obligations. Failure to adequately protect customer data exposed the company to lawsuits from affected individuals, potentially leading to significant financial penalties. Furthermore, regulatory bodies investigated the incident, leading to scrutiny of Thomas Cook’s security practices and corporate governance.
Potential Legal Liabilities
Following a data breach of this magnitude, Thomas Cook faced potential lawsuits from customers whose personal data was compromised. These lawsuits could allege negligence, breach of contract, and violations of data protection laws. Claims could include compensation for financial losses, identity theft, emotional distress, and legal costs incurred by affected individuals in mitigating the damage caused by the data breach. The scale of the breach, involving a large number of customers, significantly amplified the potential financial burden on Thomas Cook. For example, a similar large-scale data breach at a major retailer resulted in millions of dollars in settlements and legal fees.
Regulatory Actions and Investigations
Following the cyberattack, various regulatory bodies, including the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) in the UK (and potentially other international bodies depending on where the data was stored and customers were located), likely launched investigations into Thomas Cook’s handling of the incident. These investigations focused on assessing the adequacy of Thomas Cook’s data security measures, their response to the breach, and their compliance with relevant data protection regulations like the GDPR. The ICO, for instance, has the power to impose substantial fines for non-compliance with data protection regulations.
Potential Penalties and Fines
The potential penalties for Thomas Cook could have been substantial. Depending on the findings of the regulatory investigations, the company faced the possibility of significant fines for non-compliance with data protection regulations. The level of the fine would depend on several factors, including the severity of the breach, the number of individuals affected, and the effectiveness of Thomas Cook’s response. For example, the GDPR allows for fines of up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover, whichever is higher. The ICO’s track record of imposing significant fines for data breaches demonstrates the potential financial consequences for companies failing to meet their data protection obligations.
Impact of Data Protection Regulations on the Travel Industry
The travel industry, handling vast amounts of sensitive personal data, is particularly vulnerable to data breaches. Data protection regulations like the GDPR have significantly increased the compliance burden on travel companies. The following table illustrates the impact of these regulations:
| Regulation | Requirement | Thomas Cook Compliance (Post-Breach Assessment) | Industry Best Practice |
|---|---|---|---|
| GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) | Data security, notification of breaches, data subject rights | Likely inadequate prior to the breach, requiring significant improvements post-breach. Specific compliance details would need to be obtained from official reports. | Proactive security measures, robust incident response plan, regular security audits, employee training, and transparent communication with affected individuals. |
| UK Data Protection Act 2018 | Similar requirements to GDPR, with specific UK provisions | Similar to GDPR compliance assessment. Again, details would need to be gathered from official sources. | Same as GDPR best practices, emphasizing UK-specific legal requirements. |
Lessons Learned and Future Prevention: Thomas Cook Hit By Cyber Attack
The Thomas Cook cyberattack served as a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities inherent in the travel industry’s increasingly digital landscape. The incident highlighted the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures, proactive employee training, and comprehensive incident response planning. Failing to address these areas leaves companies exposed to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. This section Artikels best practices for preventing similar attacks and building a more resilient cybersecurity posture.
Preventing future cyberattacks requires a multi-faceted approach encompassing technological safeguards, employee education, and strategic planning. A robust cybersecurity strategy isn’t a one-time fix; it’s an ongoing process of adaptation and improvement in response to evolving threats.
Best Practices for Preventing Cyberattacks in the Travel Industry
Implementing robust security measures is paramount. This includes multi-factor authentication for all employee and customer accounts, regular software updates and patching to address known vulnerabilities, and the use of intrusion detection and prevention systems to monitor network traffic for malicious activity. Furthermore, employing strong encryption for sensitive data both in transit and at rest is crucial, minimizing the impact of a potential breach. Regular security assessments and penetration testing can identify weaknesses before attackers exploit them. For example, a simulated phishing campaign can reveal employee susceptibility to social engineering attacks. Finally, robust data backup and recovery plans are essential to minimize data loss in the event of a successful attack.
Improving Cybersecurity Awareness and Training for Employees
Employees are often the weakest link in a company’s cybersecurity defenses. Comprehensive training programs are vital to equip employees with the knowledge and skills to identify and avoid phishing scams, malware, and other social engineering tactics. This training should be interactive, engaging, and regularly updated to reflect current threats. Regular phishing simulations can assess employee awareness and reinforce training. Clear guidelines on acceptable use of company technology and data handling procedures should be established and consistently enforced. Furthermore, fostering a culture of security awareness, where employees are encouraged to report suspicious activity, is crucial. This proactive approach can significantly reduce the risk of successful attacks.
Designing a Comprehensive Cybersecurity Strategy for a Travel Company
A comprehensive cybersecurity strategy should be a living document, regularly reviewed and updated to reflect the evolving threat landscape. It should encompass all aspects of the organization’s IT infrastructure, including networks, applications, and data. This strategy should define roles and responsibilities for cybersecurity, establish clear incident response procedures, and Artikel processes for vulnerability management and risk assessment. Regular security audits should be conducted to verify the effectiveness of implemented controls. Budgetary allocation for cybersecurity should be commensurate with the organization’s risk profile and the value of the data it holds. For instance, a large international travel agency would require a significantly more robust cybersecurity budget and infrastructure than a small local tour operator. This necessitates a tailored approach, aligning the strategy with the company’s specific size, resources, and risk exposure.
The Importance of Incident Response Planning and Regular Security Audits
Having a well-defined incident response plan is crucial for minimizing the damage caused by a cyberattack. This plan should Artikel procedures for identifying, containing, eradicating, and recovering from a security incident. Regular security audits, conducted by internal or external experts, provide an independent assessment of the organization’s security posture, identifying vulnerabilities and recommending improvements. These audits should cover all aspects of the security infrastructure, including network security, application security, and data security. Post-incident analysis, following any security breach, is equally critical to identify weaknesses in existing security controls and inform improvements to the incident response plan and overall cybersecurity strategy. This iterative process of continuous improvement is essential for maintaining a robust and resilient cybersecurity posture.
Final Review
Source: framerusercontent.com
The Thomas Cook cyberattack serves as a stark reminder: no industry is immune to the ever-evolving threat of cybercrime. While the immediate impact was devastating, the long-term consequences – reputational damage, financial losses, and regulatory scrutiny – linger. The story underscores the urgent need for robust cybersecurity measures, proactive incident response planning, and a culture of cybersecurity awareness within travel companies. The question isn’t *if* another attack will happen, but *when* – and whether the industry will be better prepared next time.