Nominet cyber attack ivanti rce zero day – Nominet cyberattack: Ivanti RCE zero-day – sounds like a sci-fi thriller, right? Except this wasn’t fiction. A critical vulnerability in Ivanti’s software was ruthlessly exploited, leading to a significant breach at Nominet, the UK’s internet domain registry. This wasn’t just some minor data leak; we’re talking about a potentially massive compromise impacting a cornerstone of the UK’s online infrastructure. Let’s dive into the nitty-gritty of this high-stakes cyber heist and uncover what went down.
The attack leveraged a zero-day vulnerability in Ivanti’s software, meaning the flaw was unknown to the company and thus unpatched. This allowed attackers to gain unauthorized access to Nominet’s systems, potentially compromising sensitive data. The speed and efficiency of the attack highlight the ever-evolving sophistication of cyber threats and the critical need for robust security measures across all organizations. The impact extends beyond Nominet itself, underscoring the interconnectedness of our digital world and the ripple effect of such breaches.
Nominet Cyberattack Overview
Source: co.th
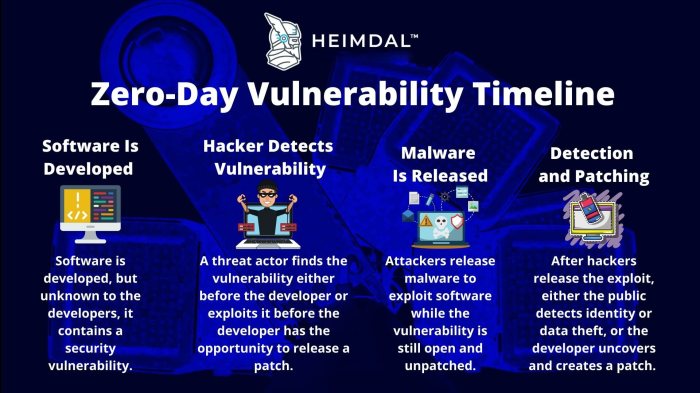
The Nominet cyberattack, leveraging a zero-day vulnerability in Ivanti’s software, highlighted the ever-present threat of sophisticated cyberattacks targeting even well-established organizations. The incident served as a stark reminder of the importance of robust security practices and proactive vulnerability management. While details remain somewhat limited due to the sensitive nature of the investigation, piecing together available information provides a clearer picture of the event’s timeline and impact.
Attack Timeline and Impact
The precise date of the initial compromise remains undisclosed, however, Nominet publicly acknowledged the attack in January 2024. The impact included unauthorized access to some of Nominet’s internal systems. While the full extent of the breach is still under investigation, the attack disrupted some services and caused significant concern within the UK’s internet infrastructure. The rapid response from Nominet and its partners ultimately mitigated further damage, preventing a potentially far more catastrophic outcome. The incident underscores the speed at which a successful cyberattack can escalate and the critical need for swift remediation.
Exploited Vulnerabilities
The attack exploited a zero-day vulnerability in Ivanti’s Endpoint Manager, specifically a Remote Code Execution (RCE) flaw. This vulnerability allowed attackers to remotely execute arbitrary code on affected systems. Zero-day exploits are particularly dangerous because they are unknown to software vendors and lack readily available patches. This means that systems are vulnerable until a patch is developed and deployed, leaving a window of opportunity for malicious actors to exploit the weakness. The severity of this RCE vulnerability allowed for significant control over compromised systems.
Attack Methods and System Access
The exact methods used by the attackers to initially gain access to Nominet’s systems remain confidential. However, exploiting the Ivanti RCE zero-day was likely a crucial step in the attack chain. Once initial access was established, the attackers may have used lateral movement techniques to expand their control within Nominet’s network. This could have involved exploiting additional vulnerabilities or leveraging compromised credentials to access other sensitive systems and data. The attackers likely aimed to achieve persistence within the network, maintaining access for as long as possible to gather information or cause further damage.
Affected Systems and Data
While the specific systems and data affected haven’t been publicly disclosed in detail, the incident involved some internal systems at Nominet. This likely includes servers, workstations, and potentially databases containing sensitive information. The confidentiality of the affected data is paramount, and the precise nature of the compromised information is likely subject to ongoing investigation. The lack of specific details reflects the sensitive nature of the incident and the need to protect ongoing investigations.
Key Actors Involved, Nominet cyber attack ivanti rce zero day
| Attacker | Victim | Role | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unknown Actors (Likely State-Sponsored or Advanced Persistent Threat) | Nominet | Victim | UK-based domain name registry; critical infrastructure provider. |
| Ivanti | N/A | Software Vendor | Provider of the vulnerable Endpoint Manager software. |
| Nominet Security Team & External Cybersecurity Experts | N/A | Responders | Responsible for containing the breach, investigating the attack, and restoring systems. |
Ivanti RCE Zero-Day Vulnerability
The Ivanti Endpoint Manager (formerly Landesk) zero-day vulnerability, exploited in the Nominet cyberattack, represents a critical threat to organizations relying on this widely used software. This vulnerability allows remote code execution (RCE), giving attackers complete control over affected systems. Understanding its technical details, potential impact, and mitigation strategies is crucial for bolstering cybersecurity defenses.
The Ivanti RCE zero-day leveraged a flaw in the software’s patching mechanism, specifically within its vulnerability management capabilities. Attackers could exploit this weakness by crafting a specially designed patch that, instead of fixing a vulnerability, installed malicious code on the target system. This malicious code then provided a backdoor for persistent access and further compromise. The vulnerability’s success hinged on its ability to bypass existing security measures and leverage the inherent trust placed in the software update process. This underscores the importance of robust security practices even for trusted software updates.
Technical Details of the Ivanti RCE Zero-Day Vulnerability
The vulnerability exploited a flaw in how Ivanti Endpoint Manager handled incoming patch files. Specifically, it allowed attackers to inject malicious code into seemingly legitimate patch packages. This code, upon installation, would execute with elevated privileges, granting the attacker complete control over the system. The precise technical details of the exploit remain partially undisclosed to prevent further exploitation, but the attack relied on manipulating the software’s internal processes to achieve RCE. The vulnerability resided in the core functionality of the software, affecting a wide range of versions and configurations.
Potential Impact on Other Organizations
The impact of this vulnerability extends far beyond Nominet. Given the widespread adoption of Ivanti Endpoint Manager across various sectors – from government agencies to large corporations – the potential for widespread damage is significant. A successful exploit could lead to data breaches, ransomware infections, network disruption, and intellectual property theft. The compromised systems could be used as stepping stones to further attacks within the organization’s network, creating a domino effect of security breaches. The scale of the potential damage is directly proportional to the number of organizations utilizing vulnerable versions of Ivanti Endpoint Manager. For example, a hospital system compromised through this vulnerability could face disruptions to patient care, potentially endangering lives.
Similar Vulnerabilities Exploited in Previous Attacks
This vulnerability shares similarities with other high-profile RCE exploits, such as the infamous EternalBlue exploit used in the WannaCry ransomware attack. EternalBlue targeted a vulnerability in Microsoft’s SMB protocol, allowing attackers to remotely execute code and spread ransomware across networks. Similarly, the SolarWinds supply chain attack involved malicious code being injected into legitimate software updates, demonstrating the devastating consequences of compromised software update mechanisms. These past incidents highlight the persistent threat posed by software supply chain attacks and the critical need for robust vulnerability management practices.
Hypothetical Exploitation Scenario
Imagine a scenario where a malicious actor gains access to a legitimate Ivanti Endpoint Manager patch distribution channel or crafts a convincing phishing email containing a seemingly legitimate patch. When a vulnerable system downloads and installs this malicious patch, the attacker’s code is executed. This code could then establish a persistent backdoor, allowing the attacker to remotely access and control the system. Further actions could include data exfiltration, installing ransomware, or using the compromised system to launch attacks against other systems within the network. This could easily cripple an organization’s operations and lead to substantial financial and reputational damage.
Mitigation Strategies
Addressing this vulnerability requires a multi-faceted approach. Here are some crucial mitigation strategies:
- Immediately apply the official Ivanti security patches to all vulnerable Ivanti Endpoint Manager instances. This is the most critical step to neutralize the vulnerability.
- Implement robust network segmentation to limit the impact of a successful compromise. Containing the attack within a limited segment of the network minimizes the overall damage.
- Strengthen endpoint security measures, including deploying antivirus and endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions. These tools can help detect and prevent malicious activity.
- Regularly review and update security policies and procedures. Proactive security measures are crucial in mitigating emerging threats.
- Employ strict access control measures to limit who can access and modify software update processes. This minimizes the risk of malicious code being introduced into the update pipeline.
- Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to identify and address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. This proactive approach helps identify weaknesses in the system before attackers can.
Impact and Response to the Attack
The Nominet cyberattack, exploiting the Ivanti RCE zero-day vulnerability, had immediate and significant consequences, impacting both Nominet’s operations and the trust placed in its services by its customers. The incident highlighted the vulnerability of even well-established organizations to sophisticated cyberattacks and underscored the critical need for robust security measures and swift incident response capabilities.
The immediate consequences included disruption to domain registration and management services, leading to potential outages and difficulties for website owners and businesses reliant on Nominet’s infrastructure. The breach also raised concerns about the potential compromise of sensitive customer data, impacting reputation and trust.
Nominet’s Containment and Mitigation Efforts
Nominet reacted swiftly to the attack, implementing a multi-pronged approach to contain the breach and mitigate its impact. This involved isolating affected systems, patching the vulnerability in their Ivanti software, and initiating a thorough investigation to determine the extent of the compromise. They also engaged with external cybersecurity experts and law enforcement agencies to assist in the investigation and recovery process. Furthermore, Nominet implemented enhanced security measures, including improved monitoring and threat detection capabilities, to prevent future attacks. Transparency was key; they communicated regularly with their customers, providing updates on the situation and the steps being taken to address it.
Comparison with Responses in Other Organizations
Nominet’s response can be compared to other organizations that have faced similar zero-day exploits. While some organizations have experienced more extensive data breaches or longer service disruptions, Nominet’s relatively swift containment and mitigation efforts, coupled with their proactive communication, stand as a positive example. The speed of patching and isolating affected systems was crucial in limiting the damage. However, comparisons are complex, as each incident has unique characteristics, including the specific vulnerability exploited, the attacker’s tactics, and the organization’s internal security posture. Some organizations might have suffered larger financial losses or faced more significant reputational damage. The crucial factor in comparison is the effectiveness of the response, measured by speed of containment, minimization of damage, and transparency of communication.
Long-Term Effects on Nominet and its Customers
The long-term effects of the attack are likely to include increased investment in cybersecurity infrastructure and personnel, potentially impacting operating costs. Nominet may also experience a period of rebuilding trust with customers, requiring ongoing communication and demonstrable commitment to enhanced security. Customers, on the other hand, may experience heightened awareness of cybersecurity risks and potentially increased scrutiny of their own security practices. The incident serves as a stark reminder of the ever-evolving threat landscape and the need for continuous vigilance. Long-term impacts might include shifts in service agreements, possibly incorporating clauses related to incident response and data breach liabilities. It also might affect the way Nominet approaches partnerships and vendors, prioritizing security certifications and risk assessments.
Incident Response Stages
| Stage | Action | Timeline | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Preparation | Security awareness training, vulnerability scanning, incident response plan development | Ongoing | Improved preparedness for future incidents |
| Detection & Analysis | Identification of the attack, analysis of the compromised systems, assessment of the impact | Days | Understanding the nature and extent of the breach |
| Containment & Eradication | Isolation of affected systems, patching vulnerabilities, removal of malware | Days to Weeks | Prevention of further damage and compromise |
| Recovery & Remediation | Restoration of systems, data recovery, implementation of enhanced security measures | Weeks to Months | Return to normal operations with improved security posture |
Security Implications and Lessons Learned
The Nominet cyberattack, leveraging the Ivanti RCE zero-day vulnerability, highlights a critical weakness in the global cybersecurity landscape. This incident underscores the interconnectedness of systems and the devastating consequences of even a single, effectively exploited vulnerability. The attack’s far-reaching implications extend beyond Nominet itself, serving as a stark reminder of the ever-evolving threat landscape and the need for proactive, multi-layered security strategies.
The successful exploitation of this zero-day vulnerability demonstrates the significant risk posed by unpatched software. The speed and scale at which attackers can leverage such vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access and disrupt operations should not be underestimated. This incident showcases the critical need for organizations to implement robust vulnerability management programs and prioritize timely patching of software across their entire infrastructure. Failure to do so leaves organizations vulnerable to exploitation, potentially resulting in data breaches, service disruptions, financial losses, and reputational damage.
Software Patching and Vulnerability Management Best Practices
Effective software patching and vulnerability management are paramount in mitigating the risk of similar attacks. This involves more than simply applying patches as they become available; it requires a comprehensive, proactive approach. This includes regularly scanning for vulnerabilities, prioritizing patches based on risk assessment, and implementing a rigorous change management process to ensure patches are deployed smoothly and without causing disruptions. Furthermore, organizations should leverage automated patching tools where feasible to streamline the process and reduce the human error factor. Regular security audits and penetration testing can further identify weaknesses and help refine the patching strategy. Consider implementing a system for tracking patch deployment and verifying their effectiveness.
Improving Threat Detection and Response Capabilities
The Nominet attack emphasizes the importance of robust threat detection and response capabilities. Organizations should invest in advanced security information and event management (SIEM) systems to monitor network traffic and identify suspicious activity. This includes implementing intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) and utilizing threat intelligence feeds to stay ahead of emerging threats. A strong security operations center (SOC) with skilled analysts is crucial for monitoring alerts, investigating incidents, and responding effectively to security breaches. Regular security drills and simulations can help prepare the SOC team for real-world scenarios, ensuring a rapid and effective response. The establishment of clear incident response plans and communication protocols is also vital.
Robust Security Awareness Training Program
A well-designed security awareness training program is essential for building a strong security culture within an organization. Employees are often the weakest link in the security chain, and educating them about cybersecurity threats and best practices is crucial. A comprehensive program should include:
- Regular training sessions covering topics such as phishing, social engineering, malware, and safe browsing practices.
- Simulated phishing attacks to assess employee awareness and reinforce training.
- Clear guidelines and policies on acceptable use of company resources and data security.
- Emphasis on password security, including the use of strong, unique passwords and multi-factor authentication.
- Regular communication and updates on emerging threats and security best practices.
- A mechanism for employees to report suspicious activity without fear of retribution.
- Ongoing reinforcement of key security concepts through regular quizzes, reminders, and newsletters.
Investing in a comprehensive security awareness training program is not just a cost; it’s an investment in protecting the organization’s valuable assets and reputation. This proactive approach is far more effective and cost-efficient than dealing with the aftermath of a successful cyberattack.
Technical Analysis of the Attack Vectors: Nominet Cyber Attack Ivanti Rce Zero Day
Source: manageengine.com
The Nominet cyberattack, leveraging the Ivanti RCE zero-day vulnerability, showcased a sophisticated attack chain relying on established techniques, albeit with a particularly effective combination. Understanding the attack vectors and the methods used to bypass security is crucial for bolstering defenses against similar threats. This analysis delves into the technical aspects, comparing the attack’s complexity to others and highlighting potential forensic evidence.
The primary attack vector was the exploitation of the Ivanti Endpoint Manager zero-day vulnerability. This vulnerability allowed remote code execution (RCE), granting attackers unfettered access to compromised systems. The attackers likely utilized spear-phishing emails or other social engineering tactics to initially deliver the malicious payload, exploiting the vulnerability through a seemingly legitimate update or software installation. This approach leverages the trust placed in established software management systems. The attackers then leveraged this initial access to pivot laterally within the Nominet network, exploiting further vulnerabilities or utilizing compromised credentials to escalate privileges and achieve their objectives.
Attack Techniques and Security Bypass
The attackers likely used several techniques to bypass security measures. This included exploiting the zero-day vulnerability before security patches were available, making traditional security solutions ineffective. Furthermore, the attackers probably employed techniques to evade detection by antivirus software and intrusion detection systems (IDS). This might have involved obfuscation of the malicious code, the use of legitimate tools for malicious purposes (living off the land), and the exploitation of known vulnerabilities in other software within the network. The success of the attack highlights the limitations of relying solely on signature-based security solutions. The use of post-exploitation techniques, such as lateral movement and privilege escalation, further demonstrates a high level of technical skill.
Sophistication Compared to Similar Attacks
The Nominet attack demonstrates a high level of sophistication compared to many other similar attacks. The use of a zero-day vulnerability significantly reduced the chances of early detection, and the successful lateral movement within the network indicates a deep understanding of the target’s infrastructure. While many attacks utilize similar techniques like spear phishing and exploitation of vulnerabilities, the combination of a zero-day, effective evasion techniques, and precise targeting sets this attack apart. Attacks like the SolarWinds supply chain compromise, while different in scope, share similarities in their sophisticated use of compromised software and persistence techniques. However, the Nominet attack appears more targeted and focused on a specific organization, unlike the broader impact of SolarWinds.
Forensic Evidence
Forensic investigators would likely have collected various types of evidence. This would include network logs showing unusual activity, such as connections to external IP addresses associated with malicious actors. System logs from compromised machines would reveal the sequence of events, including the exploitation of the vulnerability and the subsequent actions taken by the attackers. Memory dumps from affected systems could provide insights into the malicious code used and techniques employed to evade detection. Finally, analysis of the attackers’ command and control (C2) infrastructure would help to identify the perpetrators and understand the extent of the attack.
Attack Flow Visualization
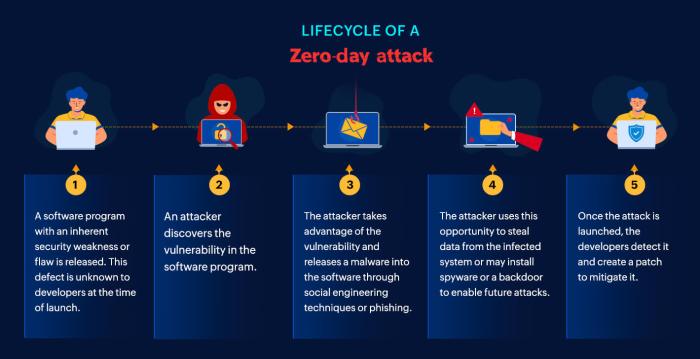
The attack likely unfolded in the following stages:
1. Initial Compromise: Spear-phishing email containing a malicious attachment or link is delivered to a Nominet employee.
2. Vulnerability Exploitation: The employee interacts with the malicious content, triggering the exploitation of the Ivanti Endpoint Manager zero-day vulnerability.
3. Initial Access: The attacker gains remote code execution on the compromised machine.
4. Lateral Movement: The attacker uses the compromised machine as a foothold to move laterally within the Nominet network, exploiting other vulnerabilities or using stolen credentials.
5. Privilege Escalation: The attacker elevates their privileges to gain access to sensitive systems and data.
6. Data Exfiltration: The attacker exfiltrates sensitive data from the network.
7. Persistence: The attacker establishes persistence mechanisms to maintain access to the network.
This simplified representation illustrates the key stages. The actual attack likely involved more complex steps and techniques, reflecting the sophistication of the operation.
Closing Notes

Source: co.uk
The Nominet cyberattack serves as a stark reminder of the ever-present threat of sophisticated cyberattacks. The exploitation of the Ivanti RCE zero-day vulnerability exposed critical vulnerabilities in software security and the importance of proactive measures. From swift incident response to robust security awareness training, organizations must prioritize comprehensive cybersecurity strategies to mitigate future risks. This isn’t just about protecting data; it’s about safeguarding the very fabric of our digital lives. The lessons learned from this incident should be a wake-up call for everyone – from individuals to multinational corporations.


