Litespeed plugin exploit rogue admins: It sounds like a hacker movie plot, right? But the reality is far more insidious. Rogue admins, those with legitimate access who turn malicious, can leverage vulnerabilities in Litespeed plugins to wreak havoc on websites. We’re diving deep into the dark side of WordPress security, exploring how these exploits happen, the devastating consequences, and – most importantly – how to prevent them. This isn’t just about technical jargon; it’s about protecting your online presence and your peace of mind.
This article unravels the common vulnerabilities in Litespeed plugins that malicious insiders exploit, detailing their methods and the potential damage inflicted. We’ll examine the motives behind these attacks – from financial gain to simple malice – and provide a practical guide to prevention and mitigation. We’ll even walk you through forensic analysis techniques to help you recover if the worst happens. Get ready to bolster your WordPress security game.
Litespeed Plugin Vulnerabilities
The seemingly innocuous world of website plugins harbors hidden dangers, especially when dealing with powerful tools like Litespeed plugins. These plugins, designed to enhance website performance and functionality, can become entry points for malicious actors if vulnerabilities exist. Understanding these vulnerabilities is crucial for website owners and administrators to maintain a secure online presence. Rogue admins, with malicious intent or compromised accounts, can leverage these weaknesses to gain unauthorized access and wreak havoc.
Rogue admins exploit vulnerabilities in Litespeed plugins through various methods, often targeting known weaknesses in code or leveraging outdated plugin versions. This can lead to a range of security breaches, from data theft to complete website compromise. The impact can be devastating, resulting in financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions.
Common Litespeed Plugin Vulnerabilities
Several common vulnerabilities plague Litespeed plugins, offering avenues for exploitation. These vulnerabilities often stem from insecure coding practices, insufficient input validation, and lack of regular updates. For example, a poorly coded plugin might fail to sanitize user inputs, allowing attackers to inject malicious code through seemingly harmless actions. Outdated plugins, on the other hand, are particularly vulnerable as security patches for known vulnerabilities are not applied.
Methods of Compromise
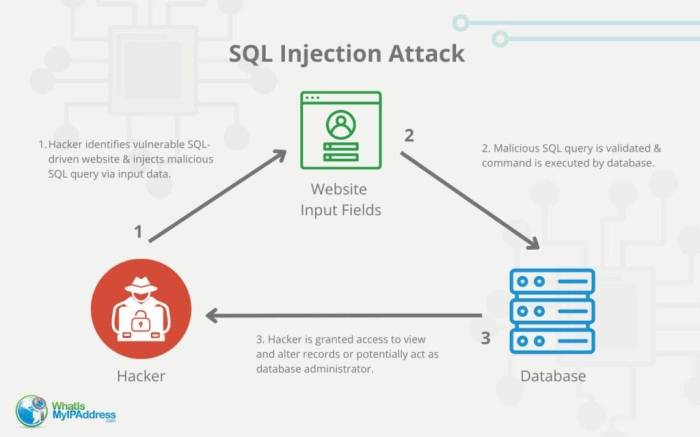
Rogue admins employ a variety of methods to exploit Litespeed plugin vulnerabilities. SQL injection attacks, for instance, remain a prevalent threat, allowing attackers to manipulate database queries to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information. Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities allow attackers to inject malicious JavaScript code into web pages, potentially stealing user credentials or redirecting users to phishing websites. Finally, exploiting known vulnerabilities in the plugin’s code, often discovered through security audits or public disclosures, provides direct access to the plugin’s functionality and potentially the entire website.
Impact on Website Security
The consequences of compromised Litespeed plugins can be severe. Data breaches, leading to the exposure of sensitive customer information, can result in significant financial losses and reputational damage. Website defacement, where attackers alter the website’s content to display malicious messages or propaganda, can severely impact user trust and brand reputation. Furthermore, compromised websites can be used as launching pads for further attacks, such as distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, targeting other websites or online services. In the worst-case scenario, a complete website takeover can lead to significant financial losses and business disruption.
Severity of Litespeed Plugin Vulnerabilities
| Vulnerability Type | Severity | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| SQL Injection | Critical | Allows attackers to execute arbitrary SQL queries against the database. | An attacker might inject SQL code into a search field to retrieve all user passwords. |
| Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) | High | Allows attackers to inject malicious JavaScript code into web pages. | An attacker could inject code to steal cookies or redirect users to a phishing site. |
| Remote File Inclusion (RFI) | High | Allows attackers to include arbitrary files from remote servers. | An attacker could include a malicious script from a compromised server. |
| Unauthenticated Access | Medium | Allows attackers to access sensitive functionalities without authentication. | A plugin might expose administrative functions without requiring a login. |
Rogue Admin Actions and Motives: Litespeed Plugin Exploit Rogue Admins
Rogue administrators exploiting vulnerabilities in LiteSpeed plugins represent a significant threat to website security. Their actions can range from minor inconveniences to catastrophic data breaches and financial losses for website owners. Understanding their methods and motivations is crucial for effective mitigation strategies. This section details common actions, malicious code examples, and the underlying drivers behind these malicious activities.
Rogue admins often leverage vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access and control over a website. This control allows them to perform a variety of malicious actions, depending on their goals and technical capabilities. The consequences can be severe, ranging from simple website defacement to extensive data theft and financial fraud.
Common Rogue Admin Actions
The actions taken by a rogue admin are directly related to their motives. However, some common actions include:
- Website Defacement: Replacing website content with offensive or politically charged material.
- Data Theft: Stealing sensitive user information, such as credit card details, personal addresses, and login credentials.
- Malware Injection: Installing malicious software that redirects users to phishing sites or infects their computers with viruses.
- Spam Distribution: Using the compromised website to send unsolicited emails, often for phishing or malware distribution purposes.
- Cryptojacking: Secretly using the website’s resources to mine cryptocurrency, slowing down the site and increasing the owner’s energy bills.
- Ransomware Deployment: Encrypting website files and demanding a ransom for their release.
- Backdoor Installation: Installing hidden access points to maintain persistent control of the website, even after the initial vulnerability is patched.
Examples of Malicious Code
Malicious code injected through vulnerable LiteSpeed plugins can take many forms. These examples illustrate the diversity and sophistication of potential attacks.
- PHP Shell Injection: A small PHP script providing remote access to the server, allowing the attacker to execute arbitrary commands. This often involves a backdoor that remains hidden after the initial compromise.
- SQL Injection Payload: Code designed to manipulate database queries, potentially allowing the attacker to extract sensitive data or modify the database structure. This could lead to data theft or website disruption.
- JavaScript Redirect: A script that redirects users to malicious websites, often designed to steal credentials or install malware on their computers. This is a common tactic for phishing attacks.
Motives Behind Rogue Admin Actions
The motivations driving rogue admins are varied, but often boil down to financial gain, reputation damage, or ideological reasons.
- Financial Gain: This is often the primary motive. Attackers might steal financial data, demand ransoms, or use the compromised website for fraudulent activities.
- Data Theft: Stealing user data for resale on the dark web or for targeted phishing campaigns can be highly lucrative.
- Website Defacement: While not directly financially motivated, this can be a form of vandalism or a way to demonstrate technical skill and cause disruption.
- Ideological Reasons: Some attackers might target specific websites or organizations due to political or social beliefs.
Flowchart of Rogue Admin Exploitation
A typical attack might follow these steps:
Imagine a flowchart with boxes and arrows. Box 1: “Identify Vulnerable LiteSpeed Plugin”. Arrow to Box 2: “Exploit Vulnerability (e.g., SQL Injection)”. Arrow to Box 3: “Gain Unauthorized Access”. Arrow to Box 4: “Install Backdoor/Malicious Code”. Arrow to Box 5: “Perform Malicious Actions (Data Theft, Defacement, etc.)”. Arrow to Box 6: “Maintain Persistence (if desired)”.
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
Source: medium.com
Securing your website against rogue admin exploitation stemming from Litespeed plugin vulnerabilities requires a proactive and multi-layered approach. Ignoring these vulnerabilities can lead to significant data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage. Implementing robust security measures is crucial for maintaining the integrity and safety of your online presence.
Effective prevention and mitigation strategies go beyond simply updating plugins. They encompass a holistic view of your website’s security posture, focusing on both technical safeguards and administrative best practices. This ensures a resilient defense against malicious actors attempting to exploit vulnerabilities within your Litespeed plugins.
Best Practices for Securing Litespeed Plugins
Several best practices significantly reduce the risk of Litespeed plugin exploitation. These practices, when implemented correctly, create a stronger security barrier against unauthorized access and malicious activities.
- Use Strong and Unique Passwords: Employ complex passwords for all administrative accounts, incorporating a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid reusing passwords across different platforms.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): 2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification, such as a code from a mobile app, in addition to the password. This significantly hinders unauthorized login attempts, even if passwords are compromised.
- Regularly Review Plugin Permissions: Carefully examine the permissions each Litespeed plugin requests. Only grant necessary permissions, minimizing the potential impact of a compromise. Regularly review these permissions to ensure they remain appropriate.
- Restrict Access to Sensitive Files and Directories: Implement measures to limit direct access to crucial files and directories, preventing unauthorized modification or deletion. This might involve using .htaccess files or other server-side configurations.
- Implement Regular Backups: Maintain frequent backups of your website’s files and database. This allows for quick recovery in case of a successful attack, minimizing downtime and data loss.
Importance of Regular Plugin Updates and Security Audits
Ignoring updates and neglecting security audits leaves your website vulnerable. Regular maintenance is paramount for maintaining a secure online presence.
- Regular Plugin Updates: Plugin developers frequently release updates that address security vulnerabilities. Staying current with these updates is crucial to patching known weaknesses before they can be exploited.
- Scheduled Security Audits: Regular security audits, conducted by qualified professionals or using automated security scanners, help identify potential vulnerabilities and misconfigurations that could be exploited. These audits provide a comprehensive assessment of your website’s security posture.
Robust Access Control Measures
Implementing robust access control measures prevents unauthorized access and limits the potential damage from a compromised account.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): RBAC assigns different permission levels to users based on their roles. This prevents users from accessing functionalities beyond their responsibilities, minimizing the risk of accidental or malicious actions.
- Least Privilege Principle: Grant users only the minimum permissions necessary to perform their tasks. This limits the potential impact of a compromised account, as the attacker will have restricted access.
- Regular User Account Reviews: Periodically review user accounts, disabling or deleting inactive accounts. This reduces the number of potential entry points for attackers.
Detecting and Responding to a Litespeed Plugin Compromise
A step-by-step guide aids in effectively addressing a compromised Litespeed plugin.
- Identify the Compromise: Look for unusual activity, such as unexpected changes to website content, unauthorized file uploads, or suspicious login attempts.
- Isolate the Affected System: Immediately isolate the affected website or server to prevent further damage and the spread of the compromise.
- Investigate the Root Cause: Determine how the compromise occurred, identifying the specific vulnerability exploited and the extent of the damage.
- Restore from Backup: Restore your website from a clean backup taken before the compromise. This ensures the removal of malicious code and the restoration of your website to a secure state.
- Strengthen Security: Implement the necessary security measures discussed earlier to prevent future compromises. This includes updating plugins, strengthening passwords, and implementing robust access control measures.
- Monitor for Further Activity: Continue monitoring your website for any suspicious activity, even after restoring from backup. This helps ensure that the compromise has been fully addressed.
Impact Analysis of Exploits
A rogue administrator exploiting vulnerabilities in a LiteSpeed plugin can unleash a cascade of negative consequences, impacting everything from your website’s functionality to your business’s reputation and bottom line. The severity of the impact depends heavily on the type of exploit and the specific actions taken by the malicious actor. Understanding these potential ramifications is crucial for effective prevention and mitigation.
The consequences of a successful LiteSpeed plugin exploit extend far beyond a simple website malfunction. Data breaches, performance degradation, and eroded user trust are just the tip of the iceberg. Exploits targeting sensitive user information can lead to identity theft, financial losses for both the website owner and affected users, and significant legal repercussions. Compromised website functionality can cripple online businesses, resulting in lost revenue and damaged brand reputation.
Website Performance Degradation
Exploits often involve injecting malicious code, which can consume significant server resources. This leads to slower loading times, increased latency, and potentially complete website outages. Imagine a popular e-commerce site suddenly becoming unresponsive – the financial impact from lost sales and frustrated customers could be devastating. The more sophisticated the exploit, the more severe the performance impact, potentially rendering the site unusable for extended periods. For instance, a denial-of-service (DoS) attack launched through a compromised plugin could overwhelm the server, causing complete unavailability.
Data Integrity and Security Breaches
A rogue admin with access through a plugin vulnerability might steal sensitive data, such as user credentials, payment information, or proprietary business data. This breach not only violates user privacy but also exposes the website owner to significant legal and financial penalties. Consider the impact on a healthcare provider’s website – a data breach exposing patient medical records could lead to hefty fines and irreparable damage to the organization’s reputation. The compromised data could also be used for further malicious activities like identity theft or blackmail.
Erosion of User Trust and Brand Reputation
A security breach, regardless of its scale, severely damages user trust. Once users lose confidence in a website’s ability to protect their information, they’re unlikely to return. This loss of trust translates directly into lost revenue and a damaged brand reputation, which can be difficult and expensive to repair. The negative publicity surrounding a data breach can spread rapidly through social media and news outlets, causing lasting damage to the website’s image and hindering future growth. For example, a well-known online retailer experiencing a large-scale data breach might see a significant drop in sales and customer loyalty for months, even years, after the incident.
Legal and Financial Repercussions
The legal and financial repercussions of a successful LiteSpeed plugin exploit can be substantial. Website owners face potential liabilities under various data protection regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA, leading to hefty fines. Furthermore, they may face lawsuits from affected users who suffered financial or reputational damage.
- Fines and Penalties: Significant financial penalties under data protection laws (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) can reach millions of dollars depending on the severity of the breach and the number of affected individuals.
- Lawsuits from Affected Users: Class-action lawsuits from users whose data was compromised can result in massive legal fees and settlements.
- Loss of Revenue: Website downtime and loss of user trust can lead to significant drops in sales and revenue.
- Reputational Damage: Negative publicity can severely damage the website’s brand reputation, impacting long-term growth and profitability.
- Insurance Claims: While cyber insurance can help cover some costs, the process of filing a claim and receiving compensation can be lengthy and complex.
Forensic Analysis Techniques
Uncovering the digital fingerprints of a rogue admin’s attack on a website leveraging a LiteSpeed plugin vulnerability requires a systematic forensic approach. This involves meticulously examining server logs, database records, and the plugin itself to reconstruct the timeline of events, identify the perpetrator, and assess the damage inflicted. The goal is to not only restore the website but also to prevent future compromises.
The investigation begins with securing the compromised system to prevent further damage. This includes isolating the affected server from the network and taking a snapshot of the system’s state using tools like `dd` or specialized forensic imaging software. This ensures that the evidence remains unaltered throughout the investigation.
Log File Analysis
Analyzing server logs is crucial for tracing the rogue admin’s actions. This includes examining Apache or Nginx access logs for unusual activity, database logs for unauthorized modifications, and LiteSpeed’s own plugin logs for any suspicious entries. Specific attention should be paid to timestamps, IP addresses, user agents, and the specific actions performed. For instance, a sudden spike in database queries involving user data or configuration files, combined with login attempts from unfamiliar IP addresses, would be strong indicators of malicious activity. Correlating these log entries with timestamps from other sources, such as email logs or security information and event management (SIEM) systems, can help build a complete picture of the attack.
Database Examination
The database, often the primary target of such attacks, needs thorough scrutiny. Forensic tools can be used to analyze database backups and identify changes made by the rogue admin. This could include adding or modifying user accounts, altering website content, or inserting malicious code. Analyzing database transaction logs helps to pinpoint the exact time and nature of these modifications. By comparing the current database state with a known clean version (a backup taken before the compromise), investigators can determine the extent of data corruption or exfiltration.
Plugin and File System Analysis
The compromised LiteSpeed plugin itself needs a detailed analysis. This involves examining the plugin’s code for any modifications, backdoors, or malicious code injections. Tools like diff utilities can be used to compare the original plugin code with the compromised version to highlight any alterations. Additionally, the file system should be scanned for any unauthorized files or directories created by the attacker. This might include hidden files, unusual processes, or modified system configurations. Hashing all files and comparing them to a known good state can reveal any tampering.
Network Traffic Analysis
Examining network traffic related to the compromised website can reveal additional clues. This includes analyzing network logs for suspicious connections, data exfiltration attempts, and communication with command-and-control servers. Network forensic tools can be used to reconstruct the network activity, identifying the source and destination IP addresses, protocols used, and the amount of data transferred. This data can help identify the attacker’s location and infrastructure.
Data Recovery and System Restoration
Once the investigation is complete, the process of data recovery and system restoration begins. This involves restoring the website from a clean backup, removing any malicious code, and updating the LiteSpeed plugin to the latest version. If a suitable backup isn’t available, data recovery techniques might be necessary, depending on the extent of the damage. This could involve recovering data from the database transaction logs or using specialized data recovery tools. Following the restoration, the system should be thoroughly scanned for any remaining vulnerabilities before returning it to normal operation.
Illustrative Scenarios

Source: techworm.net
Let’s paint a picture of a real-world scenario involving a rogue administrator exploiting a vulnerability in a LiteSpeed plugin. This isn’t just theoretical; similar incidents have occurred, albeit with different plugins and attack vectors. Understanding these scenarios helps in building stronger defenses.
Imagine a mid-sized e-commerce website, “GadgetGalaxy,” running on a WordPress platform with the LiteSpeed Cache plugin installed. An employee, Alex, with administrator privileges, harbors resentment over a recent pay cut. Alex discovers a zero-day vulnerability in a less-maintained LiteSpeed plugin module – a poorly-coded function handling user authentication. This flaw allows arbitrary code execution.
Rogue Admin Actions and Website Impact, Litespeed plugin exploit rogue admins
Alex exploits the vulnerability to gain unauthorized access to the website’s database. He uses this access to alter product prices, inserting malicious JavaScript into product descriptions. This script redirects customers to a fake payment gateway controlled by Alex, stealing credit card information. Furthermore, he modifies the website’s contact information, replacing it with his own. The impact is immediate: loss of customer trust, financial losses from stolen credit card data, and reputational damage. GadgetGalaxy experiences a significant drop in sales and faces potential legal repercussions.
Detection and Investigation of the Exploit
The initial detection comes from customer complaints about fraudulent charges and altered product information. GadgetGalaxy’s security team launches an investigation. They notice unusual database activity and unusual changes to website files. A forensic analysis of server logs reveals Alex’s actions, pinpointing the exploited plugin module and the malicious code he injected. The investigation also reveals that Alex used his administrator access to mask his actions, initially making detection more difficult. Analyzing network traffic reveals the redirection to the fake payment gateway.
Mitigation and Recovery
GadgetGalaxy immediately takes down the website to prevent further damage. They patch the vulnerability in the LiteSpeed plugin, update all other plugins and the core WordPress installation, and implement stronger access controls. They work with their payment processor to resolve fraudulent transactions and notify affected customers. A thorough security audit is conducted to identify and address any other potential vulnerabilities. They also enhance their monitoring systems to detect unusual activity in the future. Legal action is pursued against Alex.
Timeline of the Exploit
The following timeline illustrates the sequence of events:
Day 1: Alex discovers the vulnerability.
Day 2-3: Alex develops and tests the exploit.
Day 4: Alex deploys the exploit, modifying product prices and injecting malicious JavaScript.
Day 5: Customers report fraudulent charges and altered product information.
Day 6: GadgetGalaxy’s security team begins investigation.
Day 7-10: Investigation and forensic analysis, identifying the exploit and Alex as the culprit.
Day 11: Website taken down for remediation.
Day 12-14: Vulnerability patched, website restored, security measures enhanced.
Day 15 onwards: Legal action against Alex commences.
Final Thoughts

Source: bleepstatic.com
The threat of rogue admins exploiting Litespeed plugins is real, and it’s a threat that demands proactive defense. While the technical details can seem daunting, the core message is simple: stay vigilant. Regular updates, robust access controls, and a proactive approach to security audits are your best weapons. By understanding the vulnerabilities, the motives, and the potential consequences, you can significantly reduce your risk and protect your website from this increasingly common threat. Don’t wait until it’s too late; secure your WordPress site today.


