7 zip zero day exploit – 7-Zip zero-day exploit: the words alone send shivers down the spine of any security professional. Imagine a vulnerability in one of the world’s most popular compression tools, silently allowing malicious actors to infiltrate systems unnoticed. This isn’t a hypothetical threat; it’s a stark reminder of the ever-present danger lurking in seemingly innocuous software. We’ll unpack the potential consequences, explore the technical intricacies, and arm you with the knowledge to protect yourself.
This deep dive will explore the history of 7-Zip vulnerabilities, detailing common attack vectors and the types of vulnerabilities exploited. We’ll examine real-world scenarios, highlighting the potential for data breaches and theft across various industries. Crucially, we’ll Artikel practical preventative measures, from updating your software regularly to verifying file integrity, and detail strategies for detection and response should an exploit occur.
Understanding 7-Zip Vulnerabilities

Source: appstudio.ca
7-Zip, a popular open-source file archiver, isn’t immune to security vulnerabilities. While generally considered reliable, its long history and complex codebase mean occasional weaknesses are discovered, sometimes with serious consequences. Understanding these vulnerabilities is crucial for users and developers alike to ensure data security.
7-Zip Vulnerability History and Common Attack Vectors
The history of 7-Zip vulnerabilities reveals a pattern: most issues stem from improper handling of maliciously crafted archive files. Attackers exploit these weaknesses by creating specially designed 7z archives containing code that, when processed by 7-Zip, executes malicious commands on the victim’s system. This often involves leveraging buffer overflows or memory corruption vulnerabilities. While 7-Zip’s developers are generally quick to patch these flaws, the existence of zero-day vulnerabilities (those unknown to the developers) poses a significant threat.
Types of 7-Zip Vulnerabilities
Several vulnerability types can affect 7-Zip. Buffer overflows occur when a program attempts to write data beyond the allocated buffer size, potentially overwriting adjacent memory regions and leading to arbitrary code execution. Memory corruption vulnerabilities involve writing data to unintended memory locations, leading to unpredictable behavior and potential security breaches. These vulnerabilities often arise from flaws in how 7-Zip parses and handles various archive formats and their metadata. For example, a vulnerability might exist in how 7-Zip handles a specific type of compression algorithm or a particular file format within the archive.
Hypothetical Zero-Day Exploit Scenario
Imagine a sophisticated attacker discovers a zero-day vulnerability in 7-Zip’s handling of a rarely used archive format. This vulnerability allows for remote code execution via a specially crafted archive. The attacker crafts a malicious 7z file containing seemingly harmless data but also embedded malicious code designed to exploit the zero-day flaw. The attacker then distributes this archive, perhaps disguised as a legitimate file, through email attachments, malicious websites, or compromised file-sharing services. An unsuspecting user downloads and opens the archive using 7-Zip. The vulnerability is triggered, allowing the attacker’s malicious code to execute, potentially granting the attacker complete control over the victim’s system, leading to data theft, system compromise, or the installation of further malware. This attack remains undetected because the vulnerability is unknown to the 7-Zip developers and thus hasn’t been patched. The impact could range from data breaches to ransomware infections. The success of such an attack hinges on the attacker’s ability to exploit the vulnerability before a patch is released and on the user’s action of opening the malicious archive.
The Impact of a 7-Zip Zero-Day Exploit
A successful 7-Zip zero-day exploit could have devastating consequences, impacting individuals and organizations alike. The vulnerability, unknown to developers and antivirus software, allows attackers to bypass security measures and execute malicious code with potentially catastrophic results. Understanding the potential impact is crucial for implementing effective mitigation strategies.
The severity of a 7-Zip zero-day exploit hinges on the specific nature of the vulnerability and the attacker’s goals. However, the potential for widespread damage is significant, ranging from data breaches to complete system compromise. Considering the prevalence of 7-Zip as a widely used archiving tool, the potential for impact is amplified.
Real-World Examples of Similar Exploits
Numerous software vulnerabilities have been exploited in the past, offering a glimpse into the potential impact of a 7-Zip zero-day. For instance, the infamous Stuxnet worm, while not directly targeting archiving software, demonstrated the devastating potential of sophisticated malware delivered through seemingly benign software. Similarly, various exploits targeting Adobe Acrobat Reader and Microsoft Office have led to widespread data breaches and ransomware attacks. These past incidents highlight the critical need for vigilance and proactive security measures.
Data Breaches and Theft
A successful 7-Zip zero-day exploit could easily facilitate data breaches and theft. An attacker could embed malicious code within a seemingly innocuous 7z archive. When a user opens the archive, the malicious code executes, granting the attacker access to the user’s system. This access could be used to steal sensitive data, including personal information, financial records, intellectual property, or confidential business documents. The stolen data could then be sold on the dark web or used for identity theft, extortion, or other malicious purposes.
Industries Most Vulnerable
Industries that handle highly sensitive data are particularly vulnerable to a 7-Zip zero-day exploit. This includes the financial sector, healthcare, government agencies, and defense contractors. These industries often store vast amounts of confidential information, making them prime targets for cyberattacks. Furthermore, businesses relying heavily on 7-Zip for data management and transfer are especially susceptible. The widespread use of 7-Zip in various sectors underscores the potential for significant damage across a broad spectrum of industries.
Potential Impacts of a 7-Zip Zero-Day Exploit
| Impact Type | Severity | Likelihood |
|---|---|---|
| Data Breach | High | High |
| System Compromise | High | High |
| Financial Loss | High | Medium |
| Reputational Damage | Medium | High |
| Legal Ramifications | Medium | Medium |
Detection and Prevention Strategies: 7 Zip Zero Day Exploit

Source: signmycode.com
So, you’ve heard about the 7-Zip zero-day exploit and you’re understandably freaked out. Don’t panic! While the threat is real, proactive measures can significantly reduce your risk. This section Artikels practical steps you can take to bolster your defenses and keep your data safe. We’ll cover prevention, detection, and best practices for keeping your 7-Zip installation secure.
Protecting yourself from zero-day exploits requires a multi-layered approach. It’s not enough to rely on a single security measure; a robust strategy combines several techniques to create a strong defense. Think of it like building a fortress – multiple walls, towers, and moats are far more effective than just one flimsy fence.
Preventative Measures Against 7-Zip Zero-Day Exploits, 7 zip zero day exploit
Several proactive steps can significantly lower your vulnerability to 7-Zip zero-day exploits. These measures focus on minimizing the chances of malicious code execution and ensuring your software is up-to-date and secure.
- Enable Automatic Updates: This is the single most effective preventative measure. Automatic updates ensure you always have the latest security patches, minimizing your exposure to vulnerabilities.
- Practice Safe Downloading: Only download 7-Zip from the official website (7-zip.org). Beware of unofficial sources or websites that might offer modified or infected versions.
- Principle of Least Privilege: Run 7-Zip and other applications with the minimum necessary permissions. Avoid running programs as administrator unless absolutely required.
- Regular Software Updates: Regularly update all your software, not just 7-Zip. Outdated software is a common entry point for malware.
- Use a Strong Password Manager: This helps secure your accounts and prevents unauthorized access to sensitive data, should a breach occur.
The Role of Antivirus and Anti-malware Software
Antivirus and anti-malware software play a crucial role in detecting and preventing malicious activity, including zero-day exploits. While they might not always catch every zero-day, they offer a critical layer of defense.
Real-time protection monitors your system for suspicious activity and blocks potentially harmful files. Regular scans help identify and remove any existing malware. Choosing reputable antivirus software with a strong reputation and regularly updating its definitions is key.
Best Practices for Updating and Patching Software
Keeping your software updated is paramount. Patches often address vulnerabilities that attackers exploit. Here’s how to ensure you’re always running the latest versions.
- Check for Updates Regularly: Most software has a built-in update checker. Use it! Don’t wait for automatic updates – check manually at least once a month.
- Enable Automatic Updates (Where Available): Let your software update itself automatically whenever possible. This is the most effective way to ensure you have the latest security patches.
- Prioritize Security Updates: Security updates should always be a top priority. Install them as soon as they become available.
- Reboot Your System After Updates: This ensures the changes take effect properly.
Checking for 7-Zip Updates and Applying Security Patches
Updating 7-Zip is straightforward. These steps ensure you have the latest security fixes.
- Open 7-Zip: Launch the 7-Zip application.
- Check for Updates (if available): Look for an “About” or “Check for Updates” option in the menu. The exact location might vary depending on your 7-Zip version.
- Download and Install: If an update is available, download and install it. Follow the on-screen instructions.
- Restart 7-Zip (if prompted): After installation, restart 7-Zip to ensure the changes take effect.
Verifying the Integrity of Downloaded 7-Zip Files
Verifying the integrity of downloaded files ensures you’re installing the genuine, uncompromised software. This can be done using checksums.
The official 7-Zip website often provides checksums (MD5, SHA-1, SHA-256) for downloaded files. After downloading 7-Zip, use a checksum utility to calculate the checksum of the downloaded file and compare it to the checksum provided on the website. If they match, the file is likely genuine and hasn’t been tampered with. A mismatch indicates potential corruption or tampering.
Exploit Analysis (Technical Aspects – High Level)
Dissecting a 7-Zip zero-day exploit involves a deep dive into its inner workings, a process often described as reverse engineering. This isn’t about casually looking under the hood; it’s about meticulously reconstructing the exploit’s logic and understanding its malicious intent. Think of it as a digital forensic investigation, where every byte counts.
The process begins with obtaining the exploit itself. This could be a malicious file, a patch, or even just network traffic. Reverse engineers then use a combination of static and dynamic analysis techniques. Static analysis involves examining the exploit’s code without actually running it, while dynamic analysis involves running the exploit in a controlled environment (like a virtual machine) to observe its behavior. This allows researchers to identify the exact vulnerabilities being exploited and how the attacker leverages them.
Key Components of a 7-Zip Exploit
A typical 7-Zip exploit usually consists of several key components working in concert. First, there’s the trigger mechanism, which could be anything from opening a specially crafted 7z archive to interacting with a specific feature within the 7-Zip application. Next, there’s the exploit code itself, containing the instructions that leverage the vulnerability to gain control of the system. This often involves carefully crafted data structures that manipulate the 7-Zip’s internal memory management or other functionalities. Finally, a payload is often included, which is the malicious code that will execute once the attacker gains control, enabling them to steal data, install malware, or take other harmful actions.
Exploit Techniques Used Against 7-Zip
Several techniques are employed to exploit vulnerabilities in 7-Zip. One common approach is buffer overflow, where the exploit sends more data than the 7-Zip application is designed to handle, overwriting critical memory regions and potentially executing malicious code. Another method involves exploiting vulnerabilities in the way 7-Zip handles file formats, such as integer overflows or out-of-bounds reads/writes, leading to unpredictable behavior and potential crashes. A sophisticated exploit might combine multiple techniques for maximum impact, exploiting multiple vulnerabilities simultaneously to increase the chances of success and to bypass security mechanisms.
Bypassing Security Measures
Exploits often attempt to bypass security measures like data execution prevention (DEP) and address space layout randomization (ASLR). DEP prevents code from being executed in memory regions designated as data, while ASLR randomizes the location of key memory regions to make it harder to predict where code will be loaded. Sophisticated exploits might use techniques like return-oriented programming (ROP) to chain together existing code snippets within the 7-Zip application to achieve their malicious goal, effectively bypassing DEP. They might also employ techniques to defeat ASLR, such as information leaks, to locate the address of the malicious code to be executed.
Crafting a Proof-of-Concept Exploit
Creating a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit involves several steps. First, a vulnerability must be identified and understood. Next, the attacker must design the exploit code, which carefully crafts malicious data to trigger the vulnerability and execute the payload. This requires a deep understanding of the 7-Zip’s internal workings and low-level programming concepts. The PoC is then tested in a controlled environment to ensure it functions as intended. This testing phase is crucial to refine the exploit and ensure its reliability. Finally, the PoC is documented to explain the exploit’s functionality and its potential impact. This process helps security researchers understand the vulnerability and develop appropriate mitigations.
Response and Mitigation
A 7-Zip zero-day exploit can wreak havoc on a system, potentially leading to data breaches, system compromise, and significant financial losses. Effective response and mitigation strategies are crucial to minimize damage and prevent future occurrences. A swift and organized response is paramount, requiring a well-defined incident response plan and a team trained to execute it.
Responding to a 7-Zip zero-day exploit requires immediate action and a methodical approach. The initial phase focuses on containment, followed by eradication, recovery, and post-incident activity, including lessons learned and preventative measures. This process involves a blend of technical expertise and effective communication across teams.
Incident Response Steps
A successful response hinges on a series of carefully orchestrated steps. These steps should be practiced regularly through simulations to ensure a smooth and efficient response during an actual incident. Failing to plan is planning to fail, and in the high-stakes world of cybersecurity, a well-rehearsed response plan is invaluable.
- Isolate Affected Systems: Immediately disconnect the compromised system from the network to prevent further spread of the exploit. This limits the potential damage and buys time for analysis and remediation.
- Secure Evidence: Collect forensic evidence from the affected system, including logs, system files, and network traffic data. This is crucial for understanding the attack, identifying the attacker, and building a case for legal action if necessary.
- Analyze the Exploit: Determine the nature and extent of the compromise. This involves analyzing the malware, identifying vulnerabilities exploited, and assessing the impact on data and systems.
- Eradicate the Malware: Remove the malware and restore the system to a clean state. This may involve reinstalling the operating system, restoring from backups, or using specialized malware removal tools.
- Restore Systems and Data: Recover data from backups and restore affected systems to their operational state. This step should prioritize critical systems and data.
- Monitor for Further Activity: Continuously monitor the system and network for any signs of further compromise or malicious activity. This proactive approach is essential to ensure the security of the entire infrastructure.
Best Practices for Incident Response and Containment
Effective containment and mitigation rely heavily on proactive measures and well-defined procedures. Investing in robust security practices minimizes the impact of a successful exploit and improves the overall security posture. This isn’t just about reacting to attacks; it’s about creating a security-conscious environment.
- Regular Backups: Maintaining regular and reliable backups is essential for data recovery. A robust backup strategy includes multiple backup locations and frequent testing to ensure data recoverability.
- Network Segmentation: Dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments limits the impact of a breach. If one segment is compromised, the rest of the network remains protected.
- Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and can help detect and block malicious attempts, providing an early warning system.
- Vulnerability Management Program: A comprehensive vulnerability management program involves regular scanning for vulnerabilities, patching systems promptly, and implementing security controls to mitigate identified risks.
Post-Exploit Action Checklist
Following a suspected 7-Zip zero-day exploit, a structured approach is crucial. This checklist ensures no critical steps are missed, allowing for a more effective and thorough response. The goal is to contain the damage, understand the attack, and prevent future incidents.
- Isolate affected systems immediately.
- Document all actions taken.
- Gather forensic evidence.
- Analyze the attack vector and extent of compromise.
- Remediate the vulnerability.
- Restore systems from backups.
- Implement enhanced security measures.
- Conduct a post-incident review.
The Importance of Timely Patching and Vulnerability Management
Proactive patching and vulnerability management are cornerstones of a robust security strategy. Failing to patch known vulnerabilities leaves systems exposed to attacks, increasing the likelihood of successful exploitation. A proactive approach reduces the attack surface and minimizes the risk of zero-day exploits. Regular updates ensure that systems are protected against the latest threats.
The Role of Security Awareness Training
Security awareness training empowers users to identify and avoid phishing scams, malicious attachments, and other social engineering tactics often used to deliver zero-day exploits. Educated users are the first line of defense, significantly reducing the risk of successful attacks. Regular training keeps employees updated on emerging threats and best practices.
Last Point
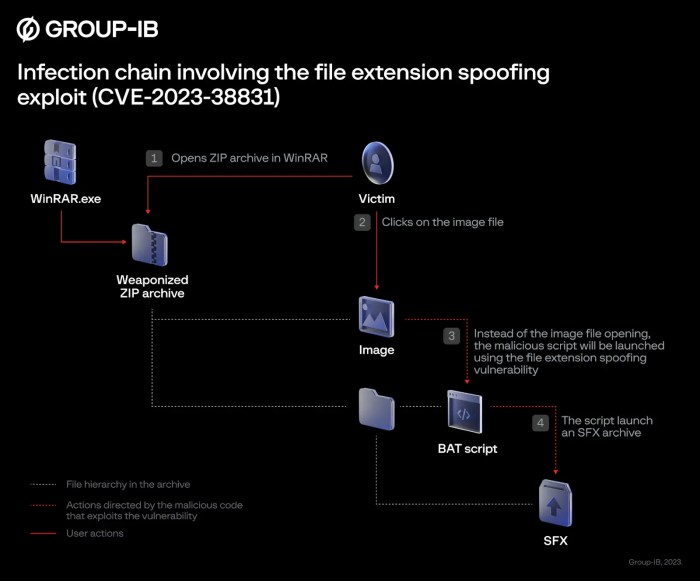
Source: arstechnica.net
The 7-Zip zero-day exploit threat underscores the critical need for vigilance in our digital landscape. While the technical details can seem daunting, proactive measures—regular updates, robust antivirus software, and a healthy dose of security awareness—are your best defense. Understanding the potential impact and knowing how to respond are key to mitigating the risks. Stay informed, stay updated, and stay safe.


